Wind: 1-44 knots from NE yesterday to W this evening as the wind increased
Sea State: up to 3 m waves breaking on west side of the island
Visibility: 5-10 NM
Sky: overcast with rain and a few sunny patches today
Temperature: 6-11 °C
Atmospheric CO2: 413.70 ppm (recorded by NOAA at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii)
It was a flurry of activity on the island yesterday. A big change from having no human visitors for a week and a half. Greg brought seven other people on the boat Second Nature. Three volunteers from the college (Lawrence, Sandra and Vincent) came to help with some maintenance and clean up tasks. John and Mike, from Pacific Coast Fire Equipment, were here to do the yearly inspection of the fire extinguishers. Warren and Ric spent almost six hours doing the electrical and plumbing hook ups and tests of the new desalinator. The desalinator room is very cramped quarters with thick concrete walls and only a six foot high ceiling inside. As Race Rocks legend goes, the building was originally constructed as a fallout shelter for Cold War fears of nuclear attack. It apparently contained emergency supplies and two bunks for the lighthouse keeper and assistant keeper. There was no space for their families. In 1975, the building was converted to a water filtration plant.
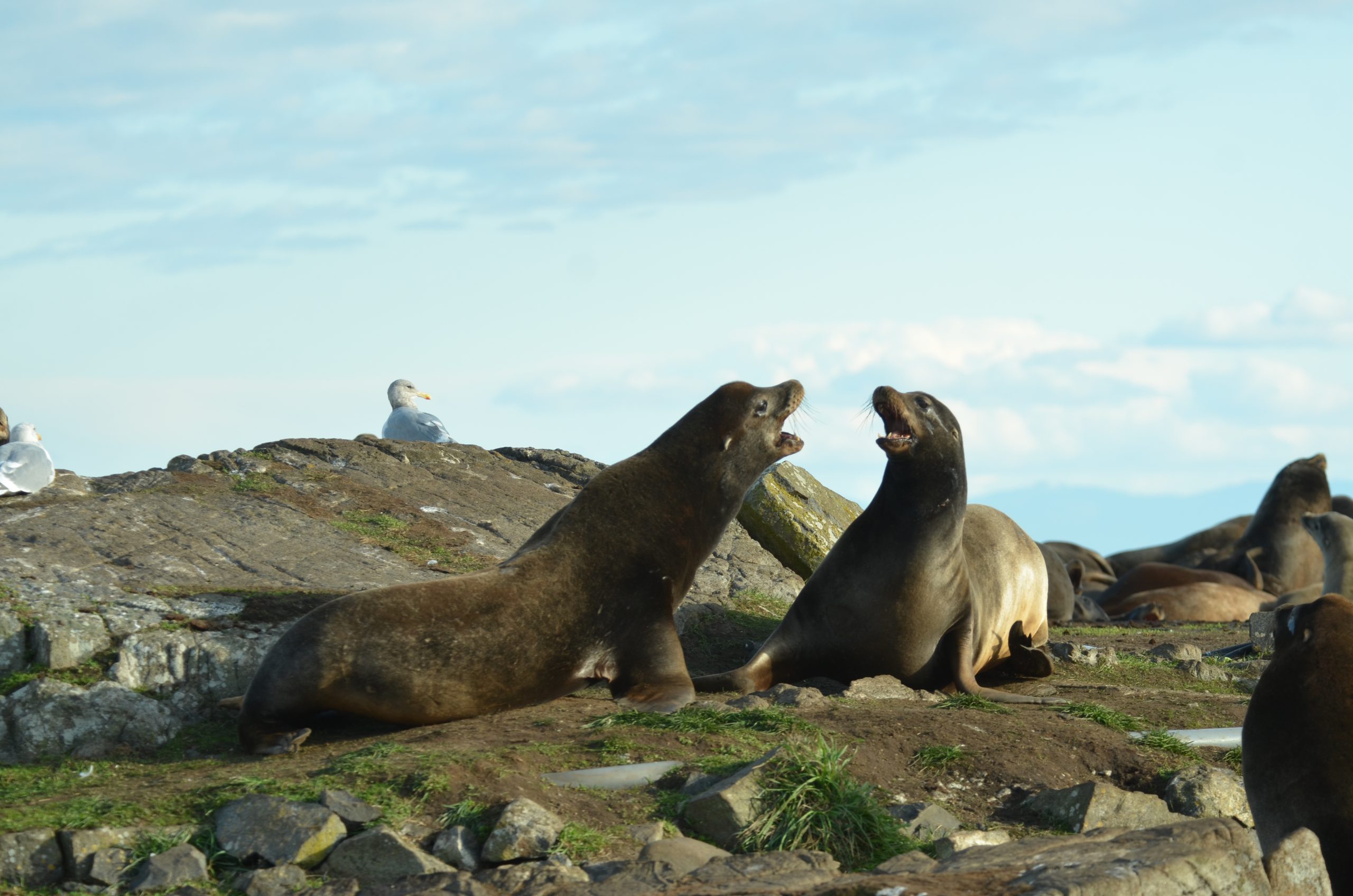
The non-human activity was busy too, with the arrival of a new adult female elephant seal. She showed up soon after the boat, staying on the boat ramp for a while before coming up to the middle of the island. The alpha male chased her around, they barked a lot, then she settled in the grassy area between the desalinator shed and the flagpole, where she still is this evening. Now there are two suspected pregnant seals hanging out in the centre of the island near the mother, pup and alpha male. The two other males appear to be keeping their distance. One is near the jetty. The other is behind the house by the compost bins.
The desalinator is running well after a total of nine hours of use. This evening, I was delighted to see that it had pumped 600 L of fresh water into the tank. Combined with the 500 L from yesterday, the desalinator has produced more fresh water than has been used since my shift began on December 21. At this rate, the 4,500 L fresh water tank should be filled up in about a week. At that point, the desalinator will be run regularly, but for shorter amounts of time. It’s an energy intensive way to produce water which consists of a reverse osmosis system and secondary UV filter. The temporary method of getting fresh water while the desalinator was out of commission was also very energy intensive. It consisted of filling up a 1,000 fresh water tank at the college, boating it to the island, and pumping it up to the tank from the boat. The water usage is planned to increase a little bit in the near future, due to some much needed pressure washing of the exteriors of the buildings, to prevent them from being overtaken by algae.
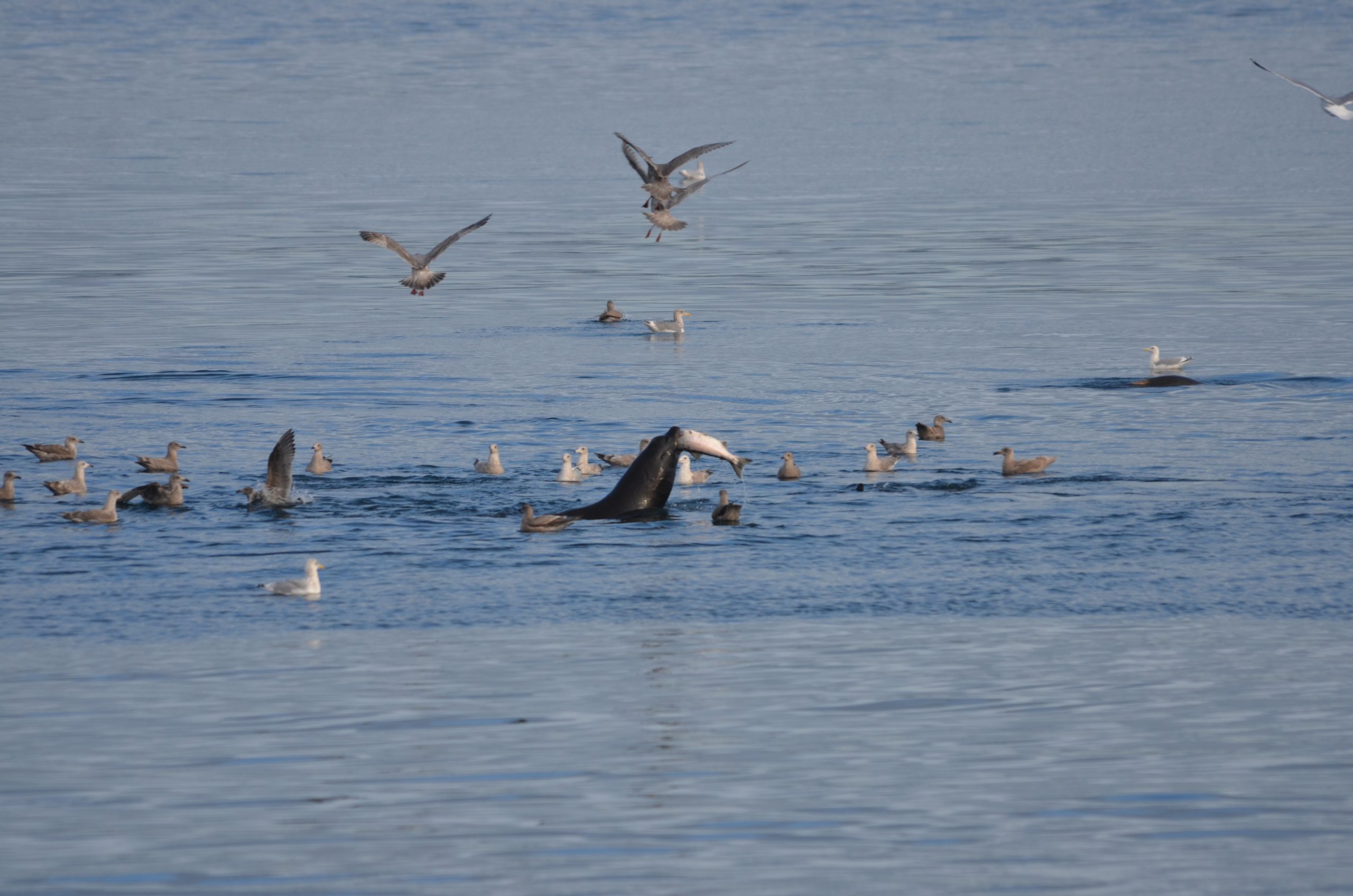
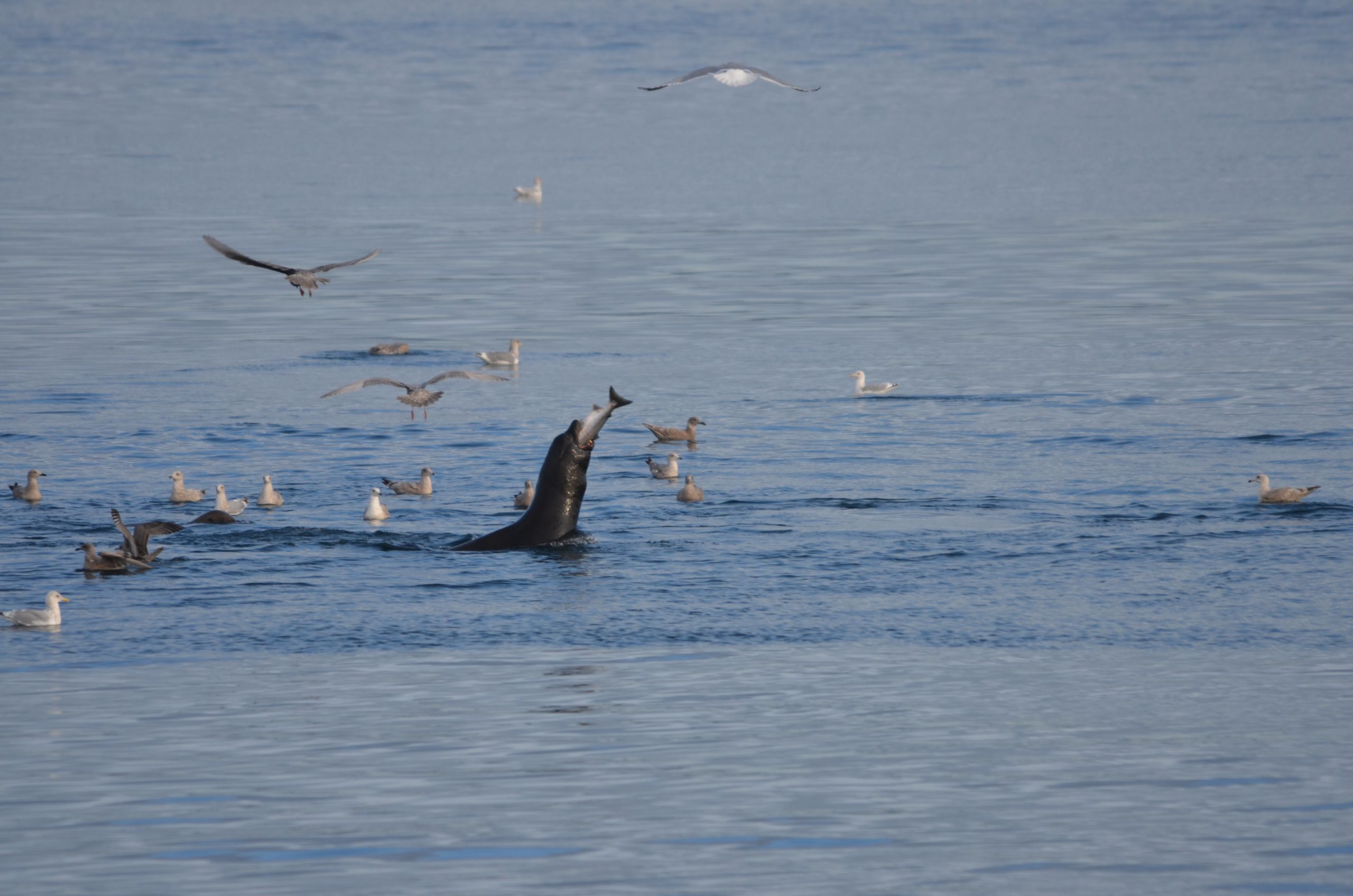
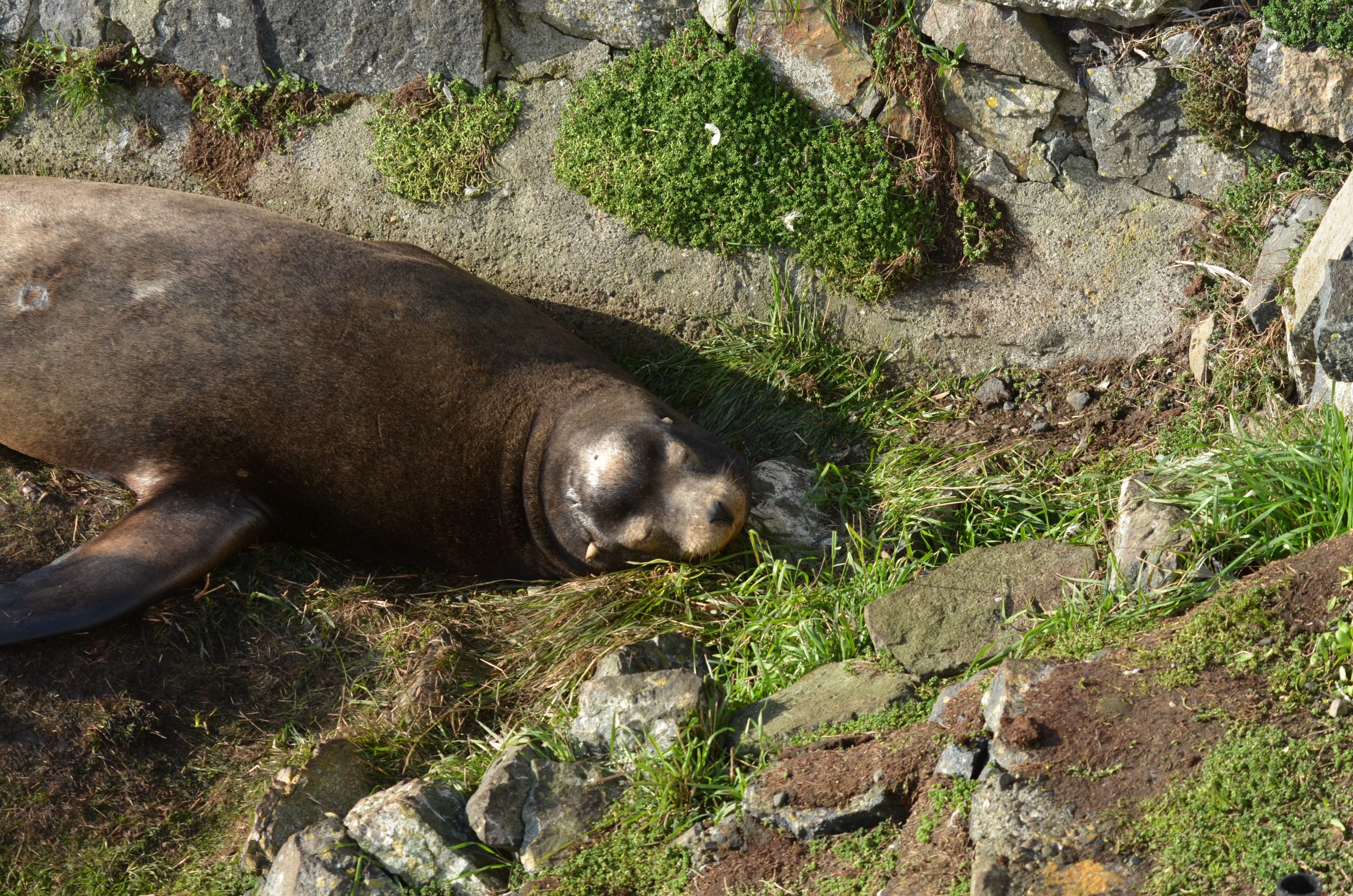
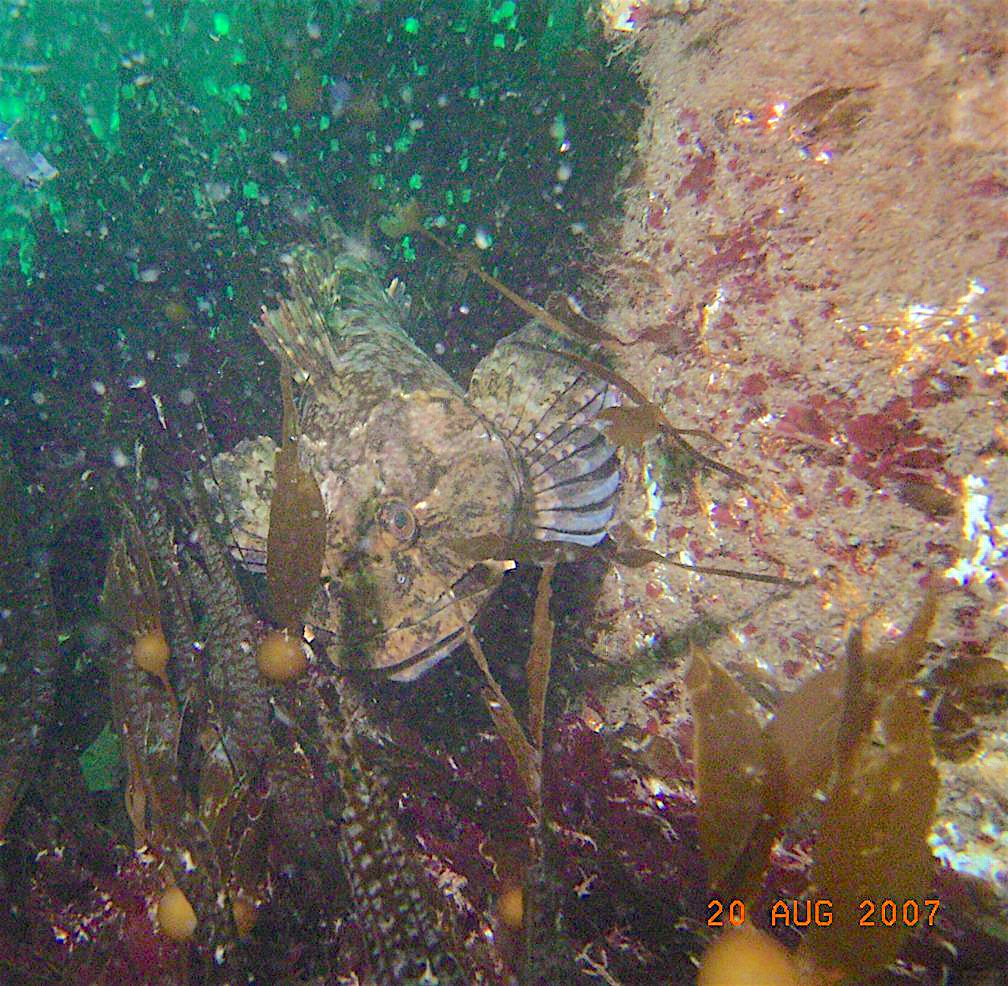
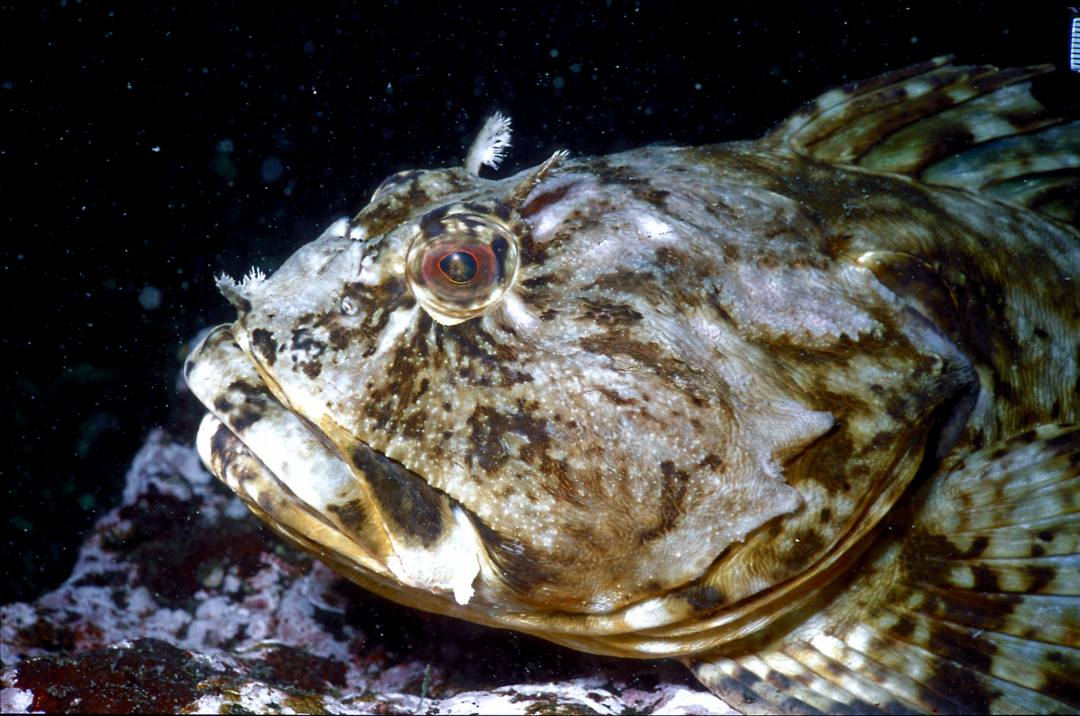
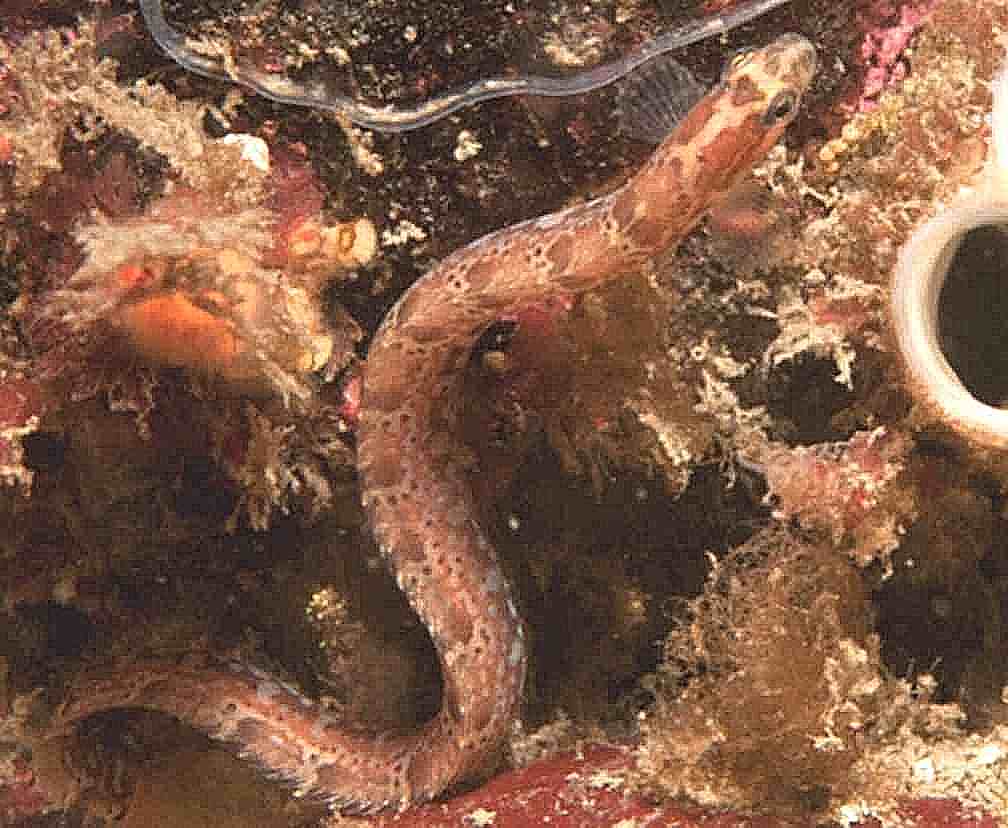
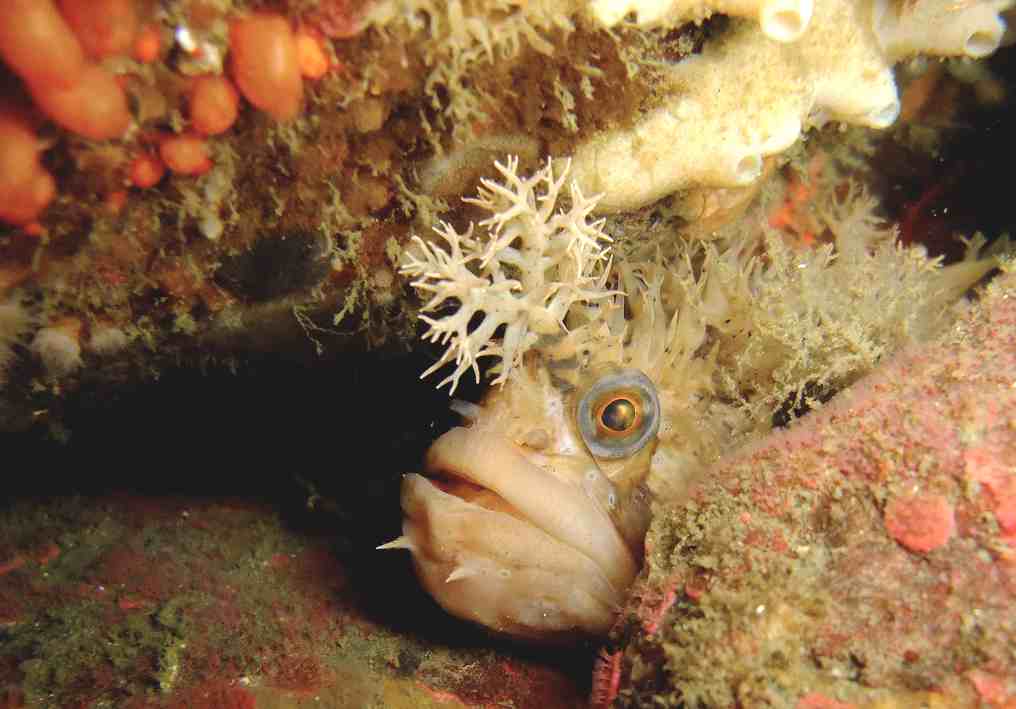
See the photos below for some recent views on the island.
-

-
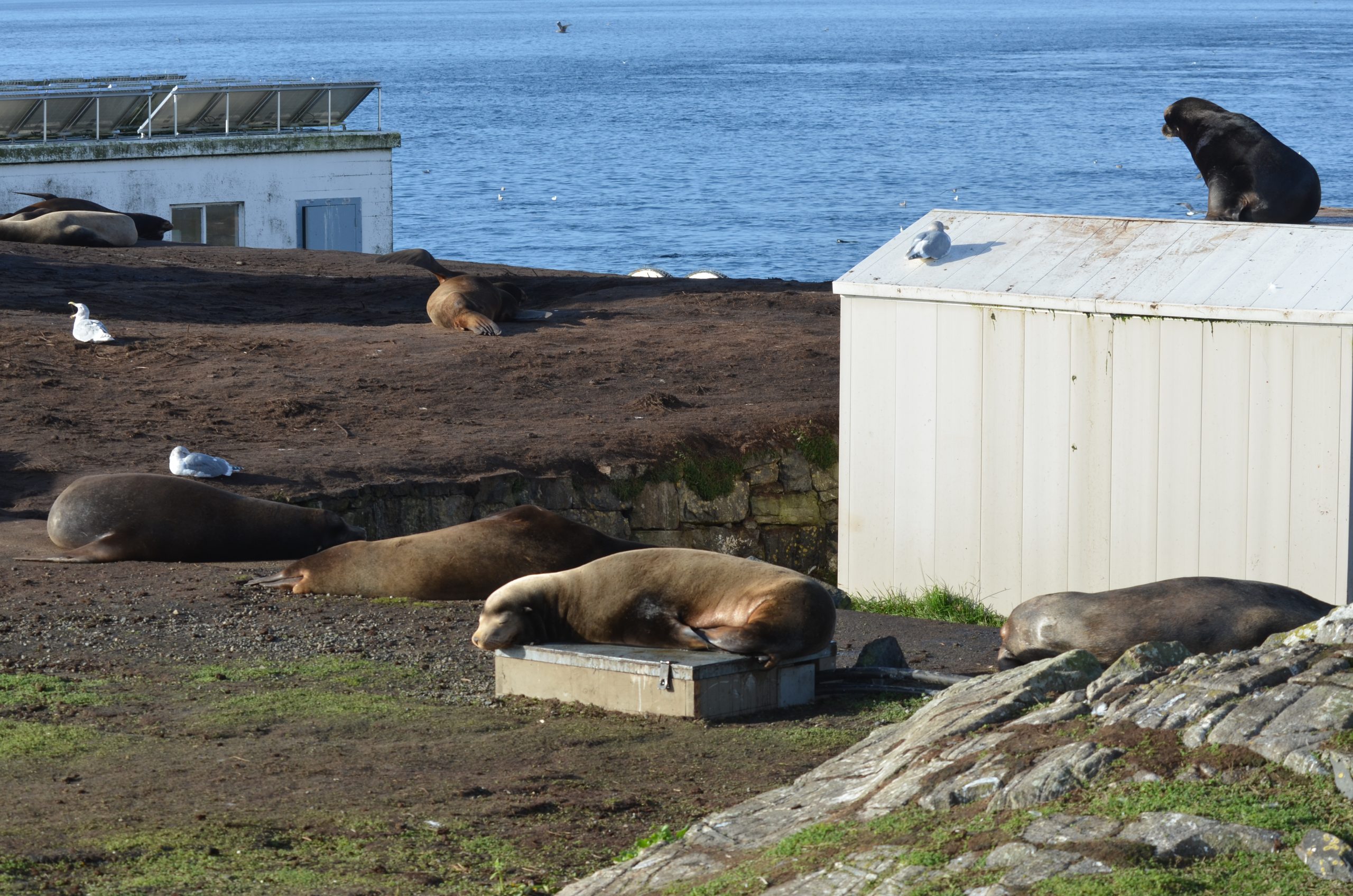
One of these things is not like the other! A large male elephant seal is in the seal lion cuddle puddle on the jetty.
-

-
Elephant seal count: 3 females, one alpha male, one pup
Not pictured: 2 males
-

-
23 black oystercatchers and one whimbrel trying to fit in
-

-
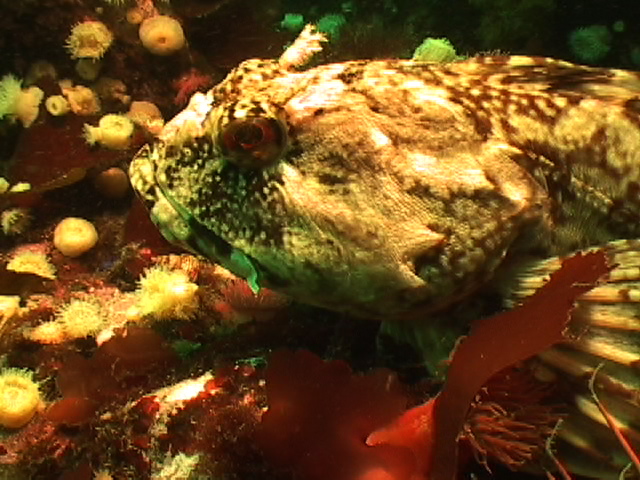
I was surprised by this large fish head that was lying amongst the rocks. Perhaps it was discarded from a fishing boat, then washing ashore, or it was was picked up by a bird.
-

-
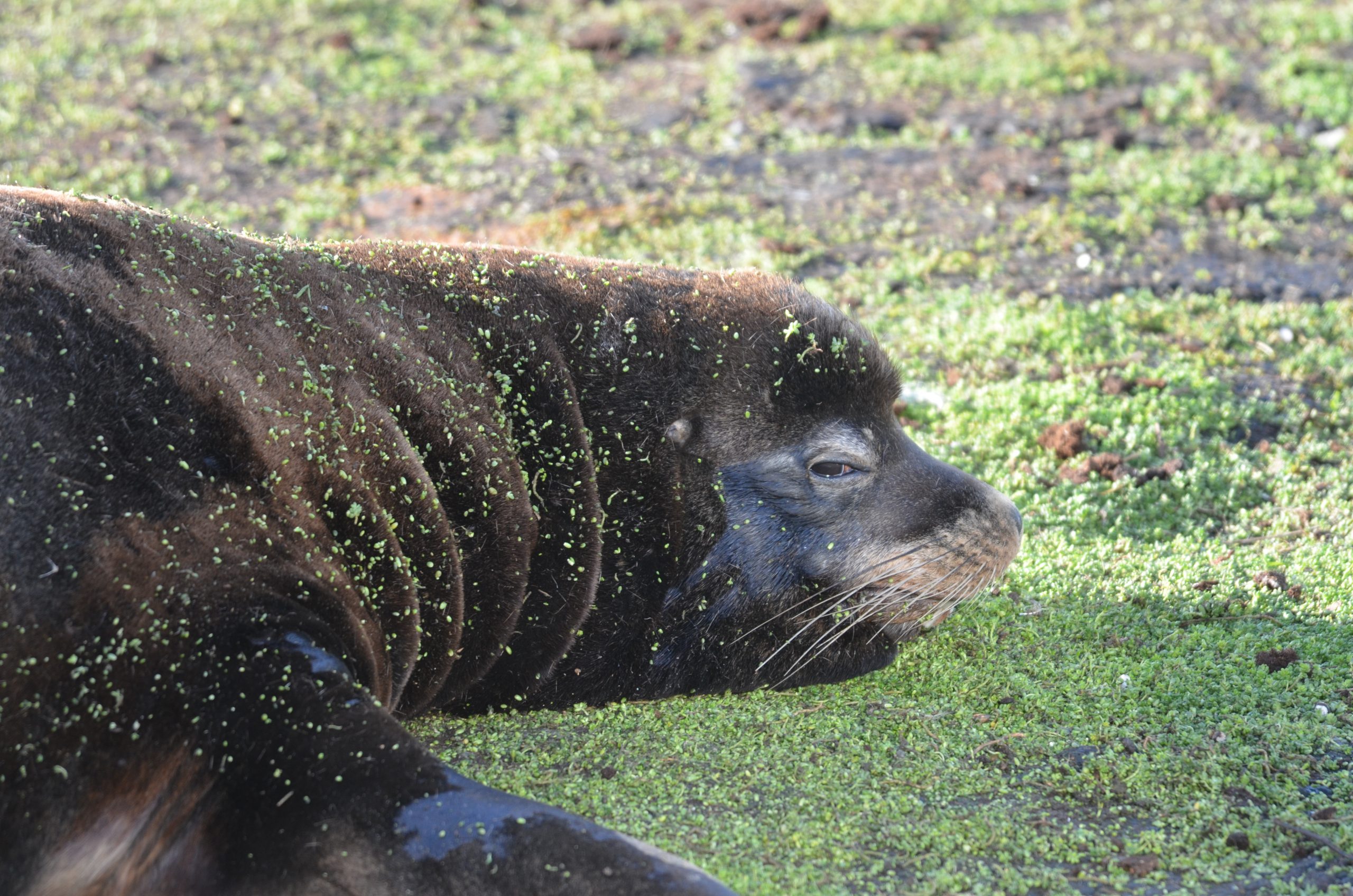
The elephant seal pup has taken to sleeping on its back.