| Lightning is a very rare occurrence on this part of the Pacific North West Coast, however we show below a method of recording lightning strikes which can be used to compare with other regions of North America. The unusual thing about lightning is that it can occur here in the Strait of Juan de Fuca in what is the winter months in North America. When lightning is never recorded in the interior…at least of Canada. |
| We are interested in noting Lightning as an abiotic factor because it contributes to the sum total of Atmospheric Nitrogen Fixation and is therefore an important feature for all organisms which are dependent on nutrients from the Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen fixation involves Nitrogen, which is a relatively inert gas, which is plentiful in air, being made to combine chemically with other elements to form more reactive nitrogen compounds such as ammonia, nitrates, or nitrites. |
| This space is reserved for the first person to record a lightning strike from the remote control cameras at Race Rocks! |
OBJECTIVES: After doing this assignment, students will be able to:a) Find out where lightning strikes are presently occurring in North America.
b) Evaluate the importance of lightning in the Nitrogen Cycle.
c) Enumerate the other abiotic effects on organisms of lightning strikes. |
Procedure:1. The enormous energy of lightning breaks nitrogen molecules and enables their atoms to combine with oxygen in the air forming nitrogen oxides. These dissolve in rain, forming nitrates, that are carried to the earth. Atmospheric nitrogen fixation probably contributes some 5– 8% of the total nitrogen fixed. See the table below for a comparison of sources of Nitrogen Fixation. The major conversion of N2 into ammonia, and thence into proteins, is achieved by microorganisms in the process called nitrogen fixation (or dinitrogen fixation). Give examples of how this process is essential for life. Include the connection between the muscle in your arm and the process of Nitrogen Fixation.
In this picture.. Alex Chan PC yr 32 is trying to get the nitrogen fixing Lathyrus or Beach Pea lined up with Tower at Race Rocks. Check the Beach Pea file to see how well he did.
Alex Chan PC yr 32 is trying to get the nitrogen fixing Lathyrus or Beach Pea lined up with Tower at Race Rocks. Check the Beach Pea file to see how well he did.
2.See the file on Biogeochemical Cycles , and construct a Nitrogen cycle from the Race Rocks image clips.
3. The Weather Office of the Government of Canada presents updates of the lightning strikes in North America
Record the Frequency and Location of Lightning strikes on three separate days when you view this link.
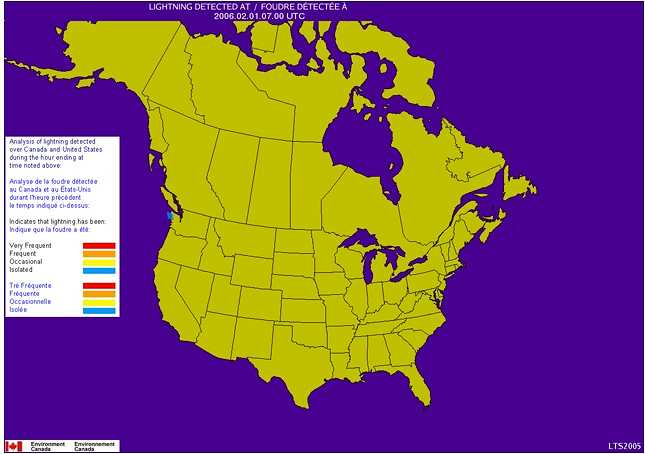
4. Click on the prerecorded sample maps below which show the location and intensity of lightning strikes in the area of the Strait of Juan de Fuca over the period of an hour. In the legend to the left, the estimated frequency of Lightning is depicted as flashes per 1000 square km* per minute as follows:
- Very Frequent (Red) = more than 6 per minute
- Frequent (Orange) = 3.0-5.9 per minute
- Occasional (Yellow) = 1.5-2.9 per minute
- Isolated (Blue) = less than 1.4 per minute
Note*: 1000 square km represents a circle having a radius of 17.8 km
|
|
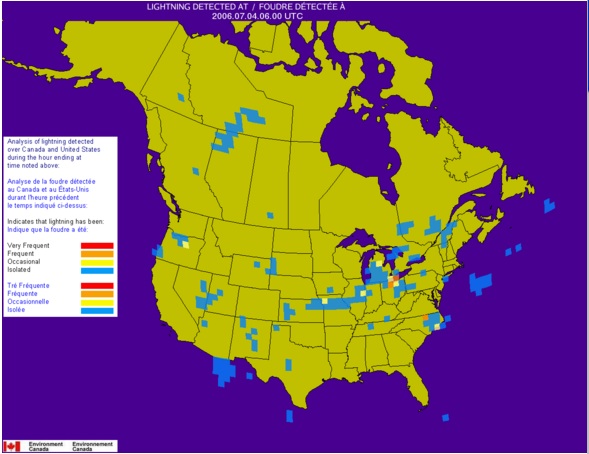
In the image to the right, you can see the contrast in frequency and intensity of strikes on a July evening. |
 “> “> |
|
January 31, 2006 2300 hrs
|
|
|
July 3, 2006 1100hrs |
| The Data below is from various sources, and has been compiled by DF Bezdicek & AC Kennedy, in Microorganisms in Action (eds. JM Lynch & JE Hobbie). Blackwell Scientific Publications 1998. It appears in the website: The Microbial World: |
N2 fixed (1012 g per year, or 106 metric tons per year) |
| Type of Fixation |
|
| Non-Biological |
|
| Industrial |
about 50 |
Combustion
|
about 20 |
| Lightning————–Compare with these other sources ——————-> |
about 10 |
| Total |
about 80 |
|
|
| Biological |
|
Agricultural land
|
about 90 |
Forest and non-agricultural land
|
about 50
|
Sea
|
about 35
|
| Total |
about 175 |
| 5. Extension..for further investigation: Find out why lightning is rare in the winter time in North America, but common in many areas in the summer. If you are from one of these areas that experience many lightning strikes, determine why they are abundant in some areas and not in others. Might you advance an hypothesis on how seasonal differences in Lightning Strikes could affect productivity of plants?( You might want to consider what grows in winter before you jump to conclusions here!) |