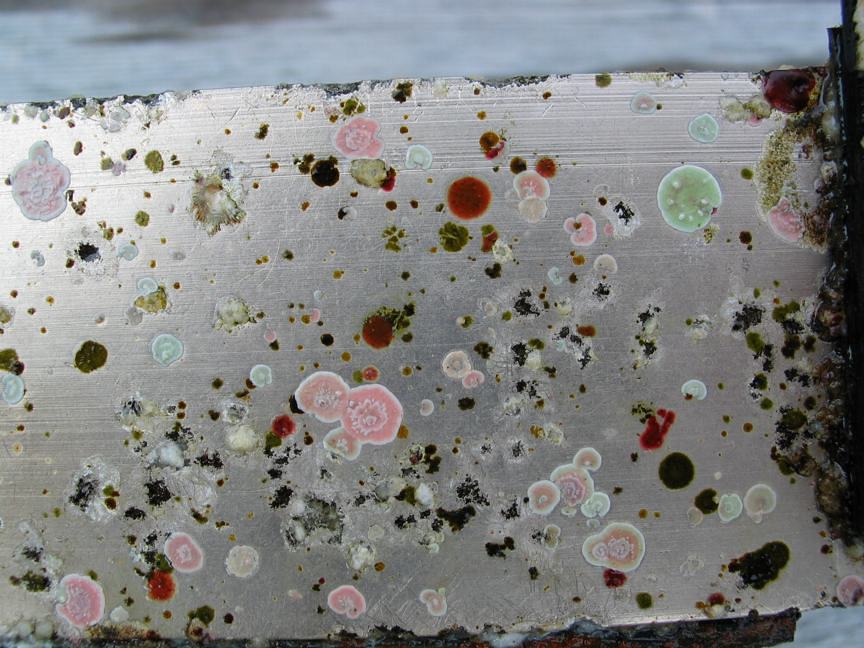
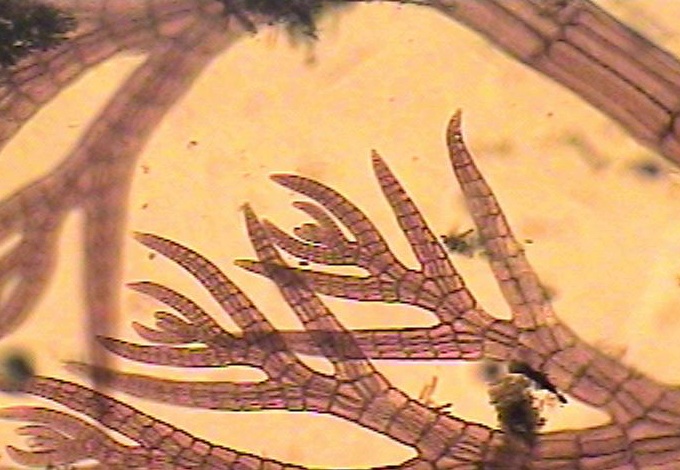
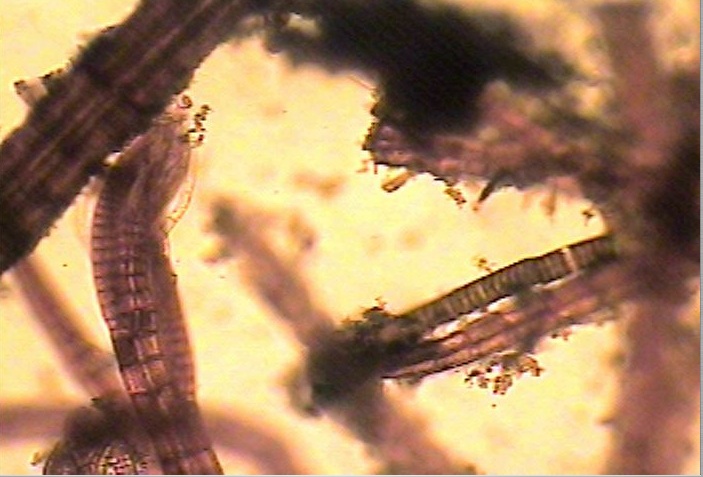
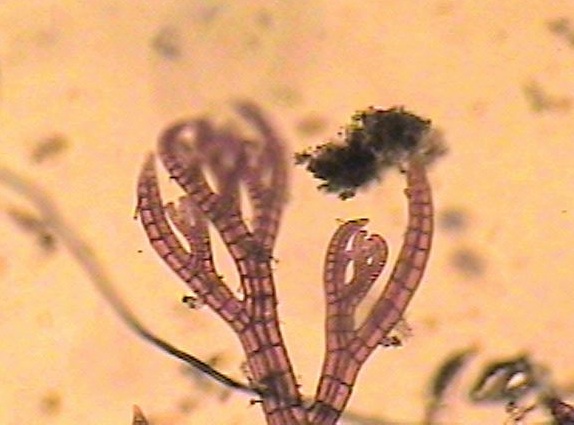
When installing equipment underwater in a high current zone where the water is laden with nutrients from upwelling as it is at Race Rocks, it becomes obvious very soon that any new substrate placed underwater becomes an instant habitat for the settlement of many invertebrate and algal species. For this page I have brought together different examples from the work we did over the years at Race Rocks. . It should be noted that the word “fouling”is a rather perjorative term, seen from the point of view of a natural process interfering with human wishes. However, it simply represents ecological succession, a perfectly natural event in a highly productive environment, and too bad that it inconvieniences us!
This video from 2001 shows what the condition of the growth of life was on a sensor bar that we installed in water at 8 meters depth just off the Jetty at Race Rocks: The sensors were for monitoring Oxygen, salinity, ph, and turbidity. Without constant attention by our divers getting accurate data from sensors like these over a long term would not be possible. This video was taken after three months in the water .
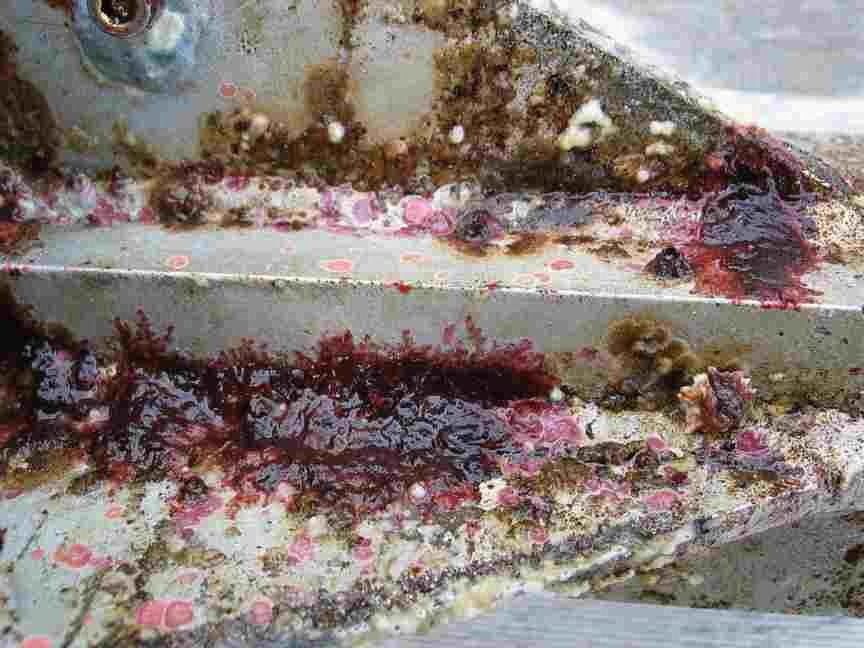
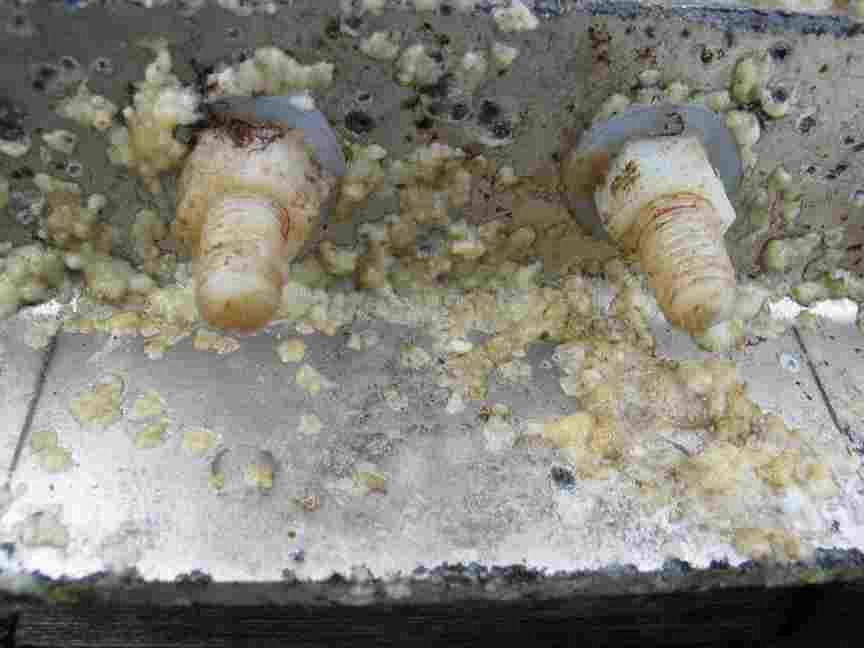
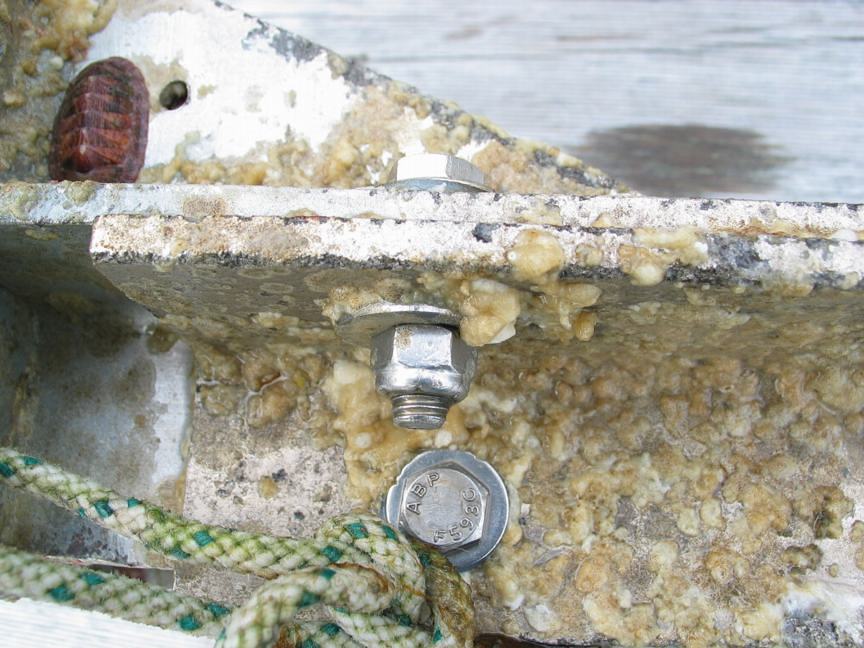
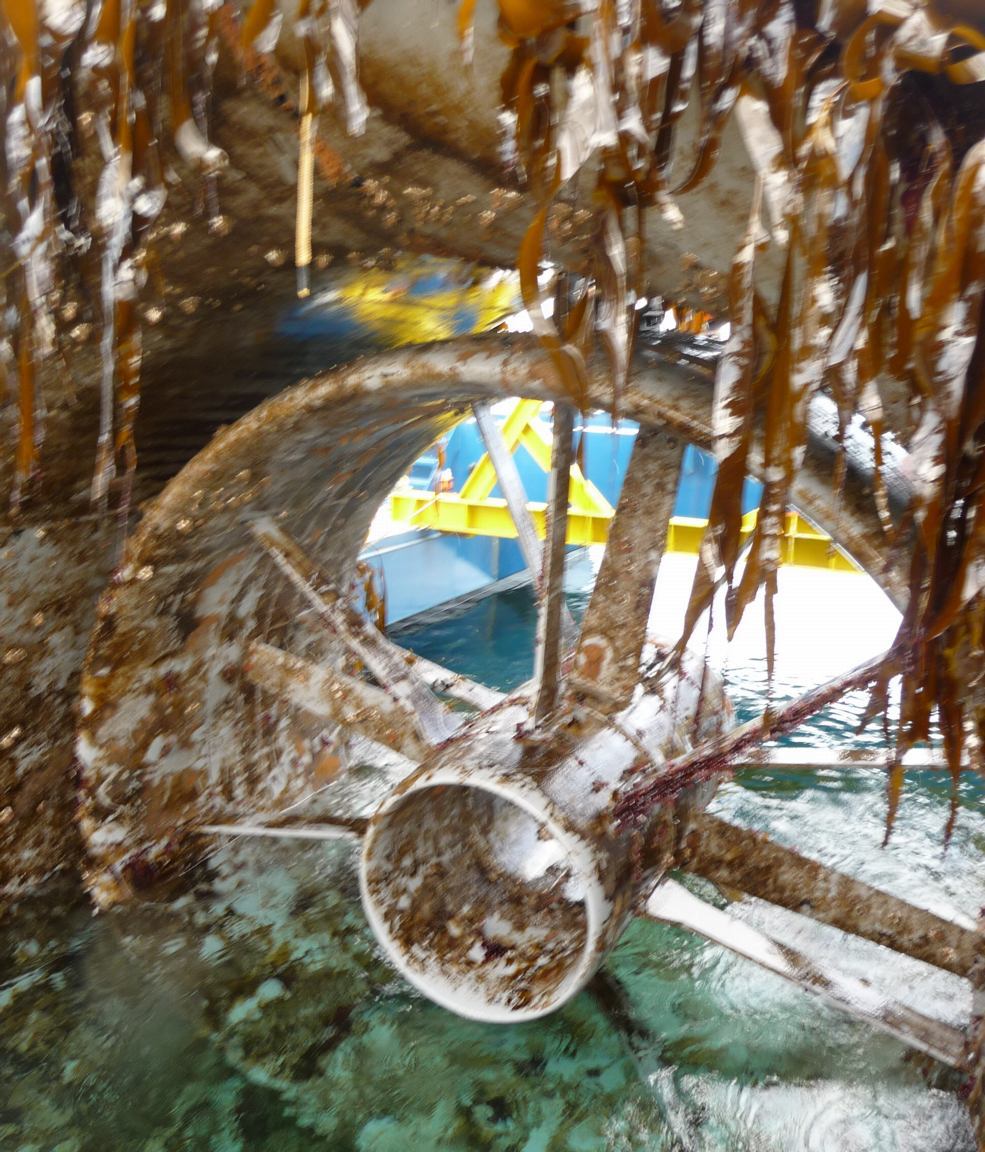 In September of 2011 we ended the experimental Tidal energy Project at Race Rocks. This file has images of the turbine covered in fouling organisms when it was raised for the final time:
In September of 2011 we ended the experimental Tidal energy Project at Race Rocks. This file has images of the turbine covered in fouling organisms when it was raised for the final time:
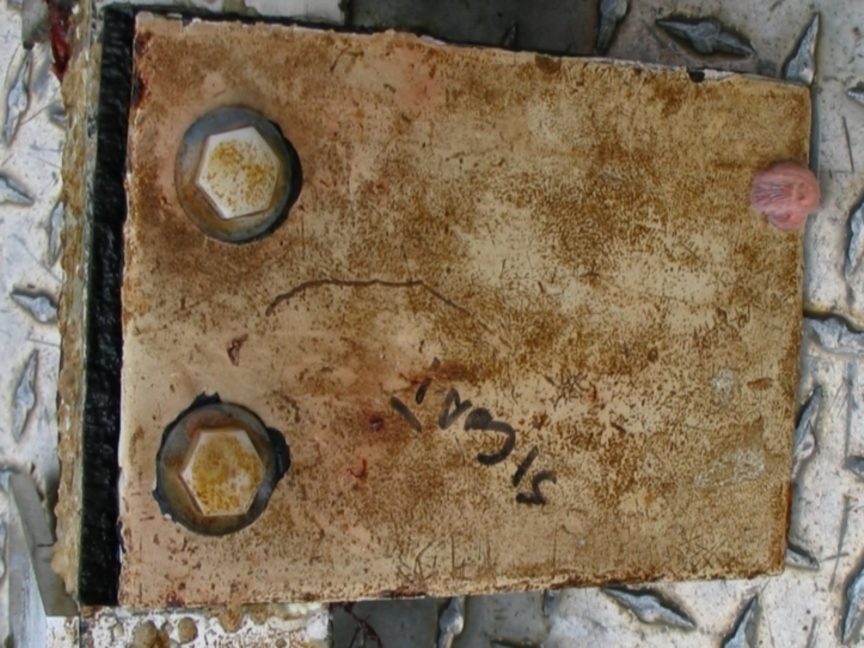
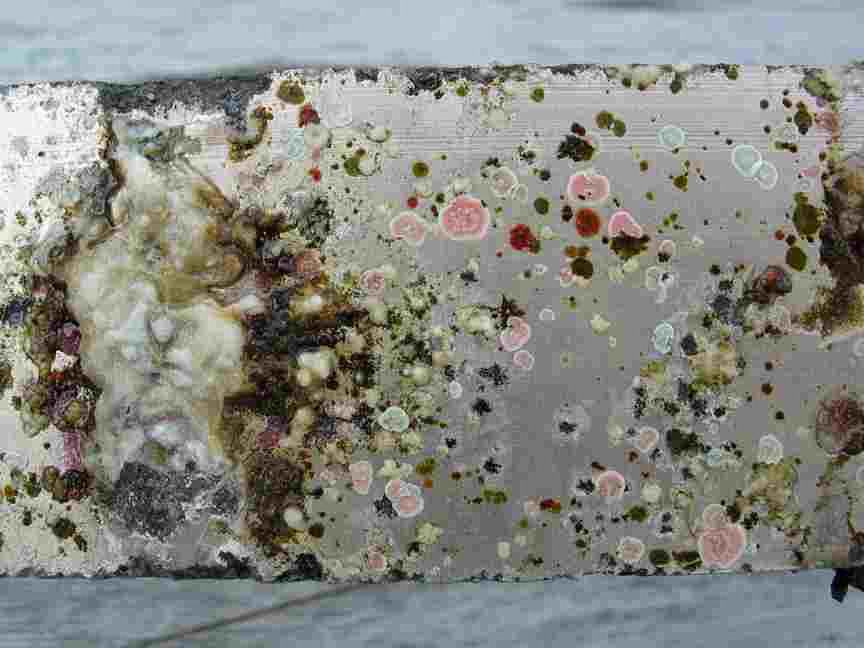
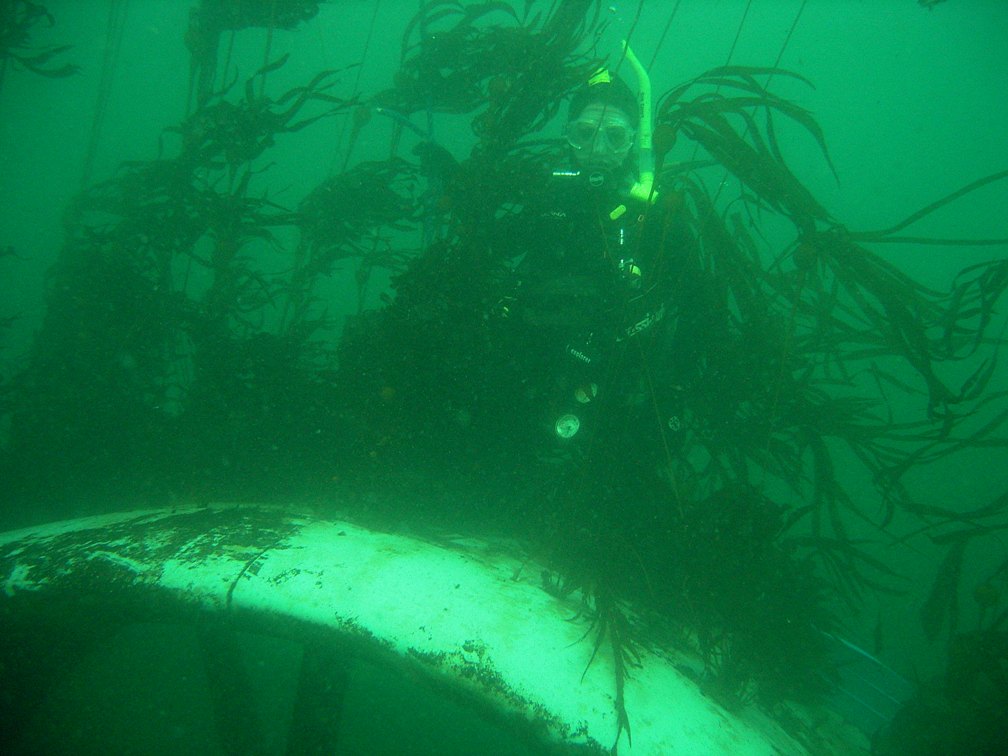 Examination of the tidal energy installation after being installed for 6 months
Examination of the tidal energy installation after being installed for 6 months
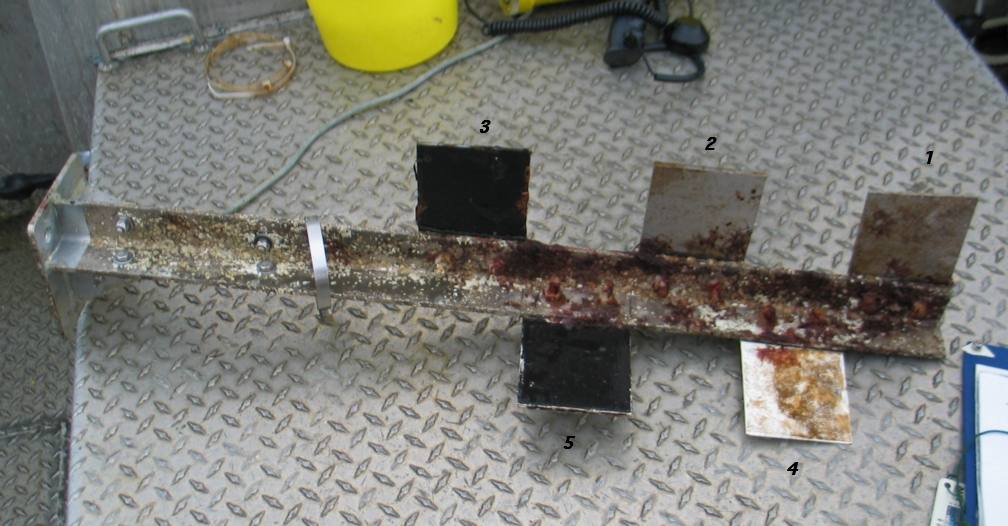
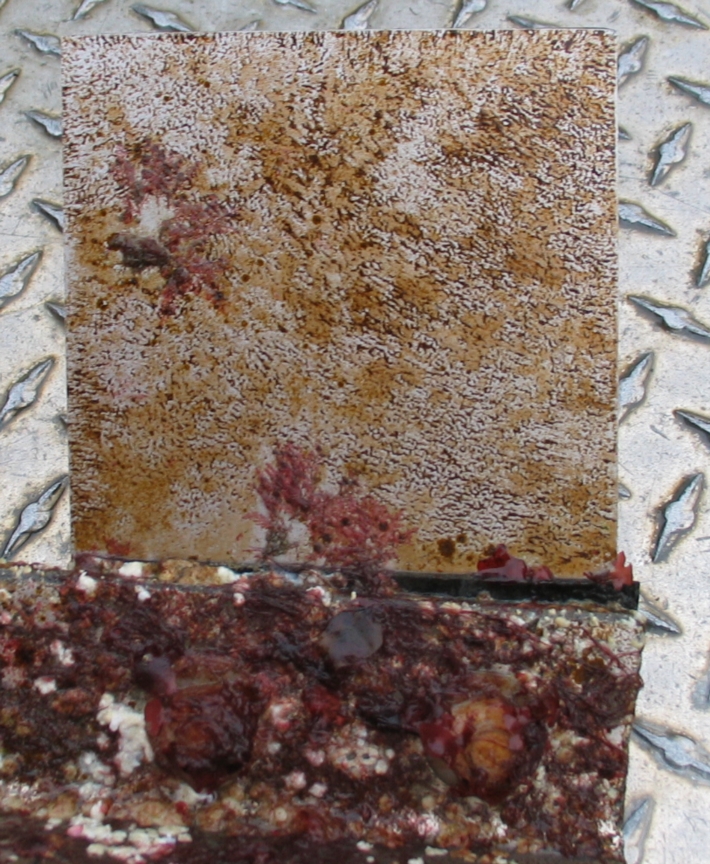
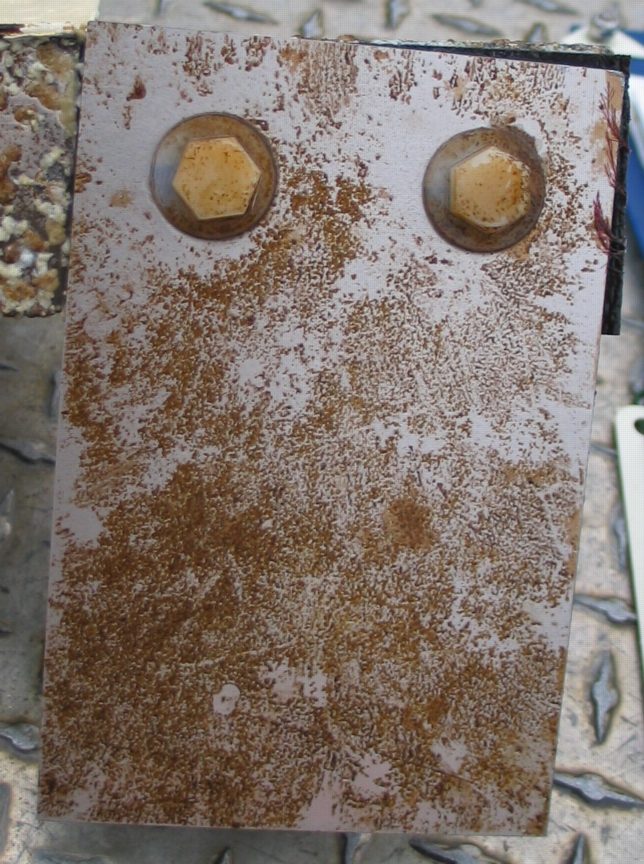
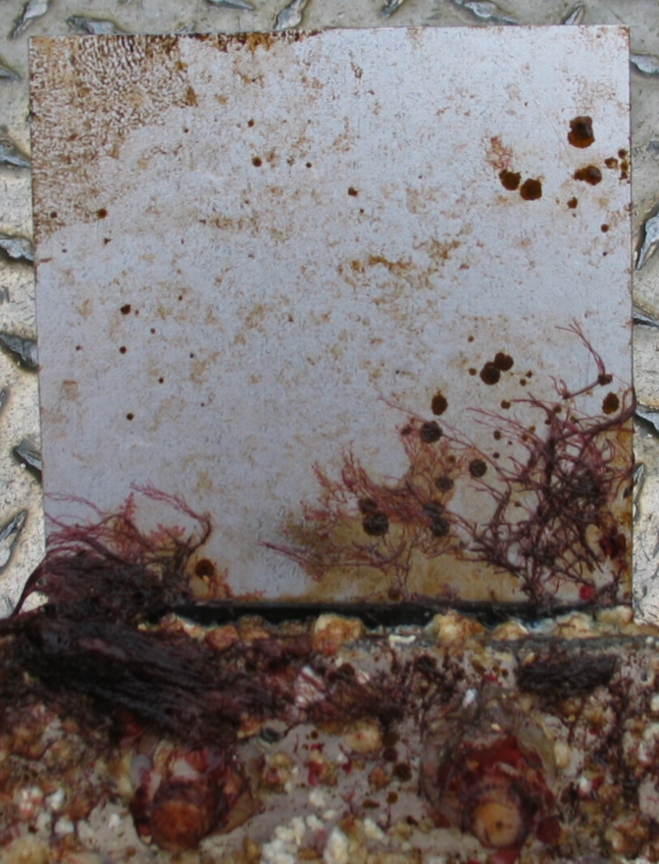
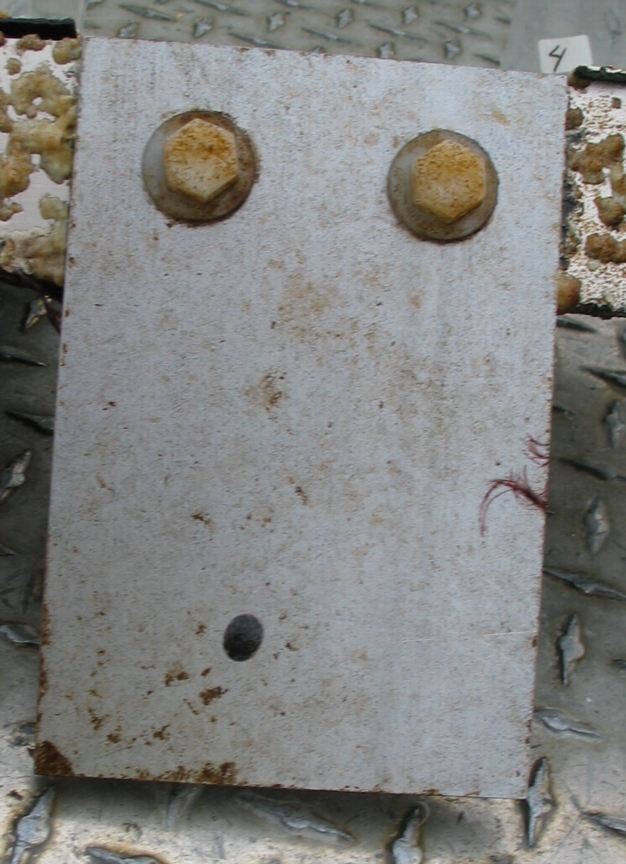
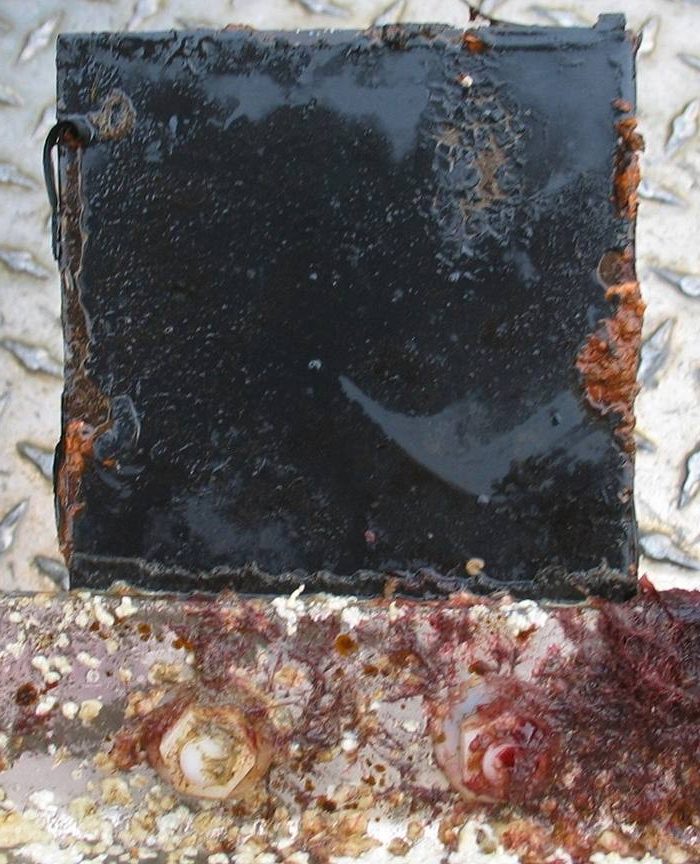
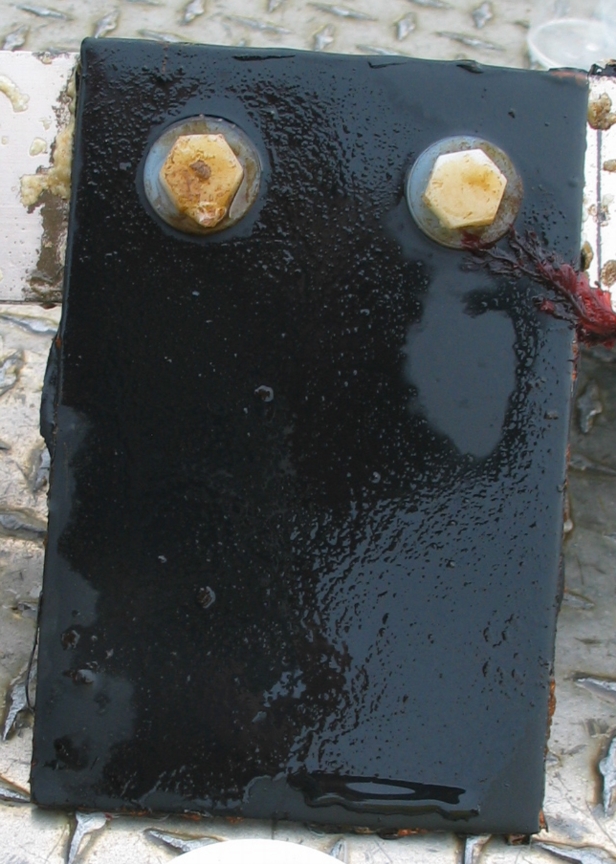
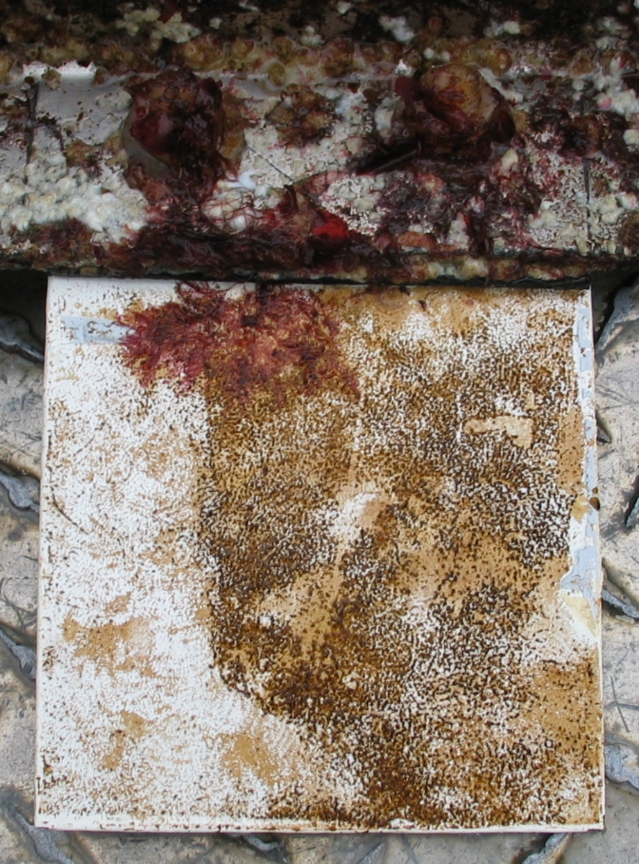
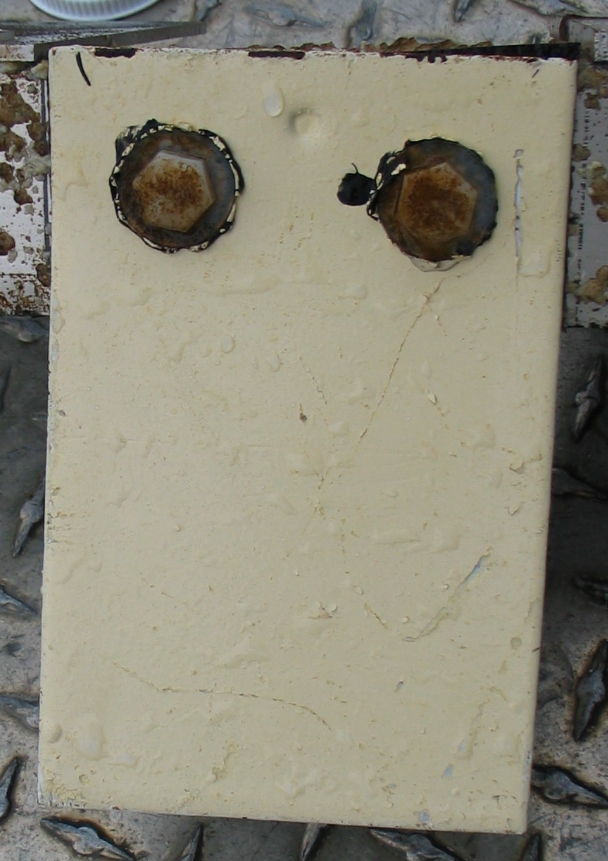
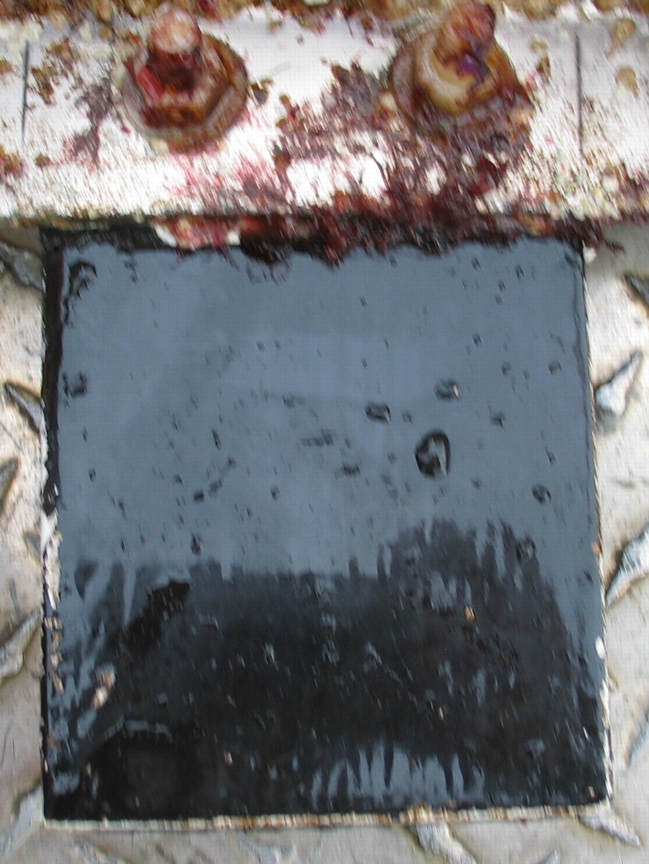
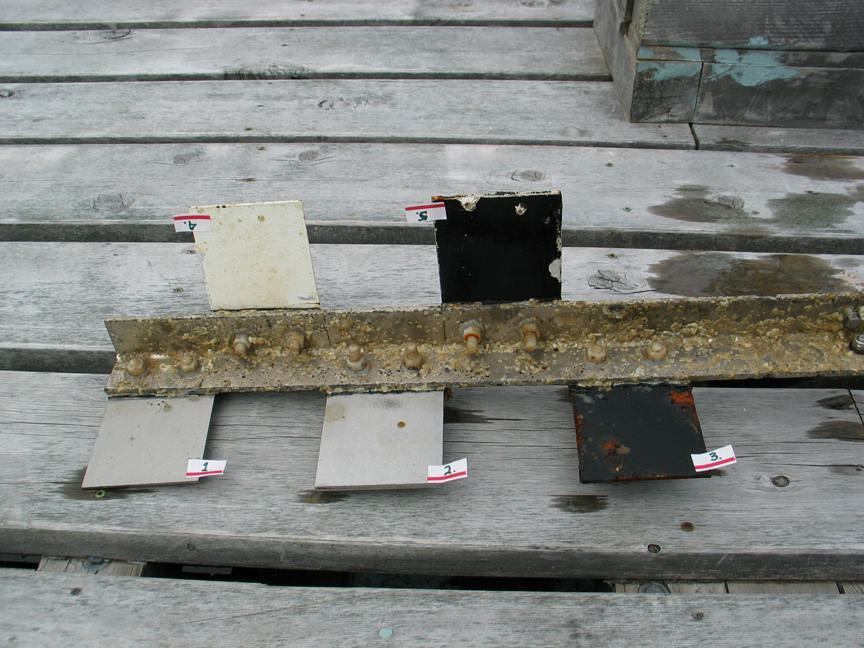
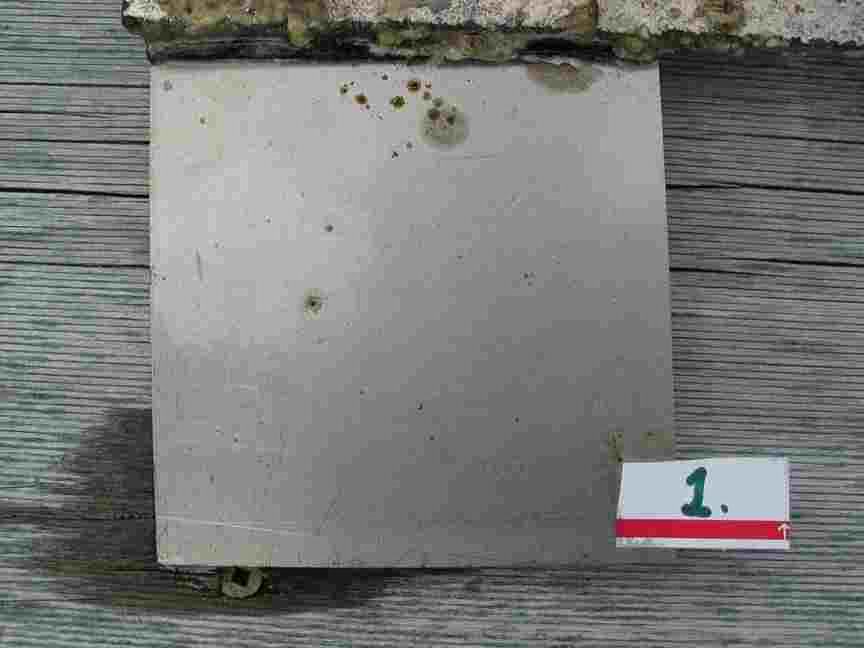
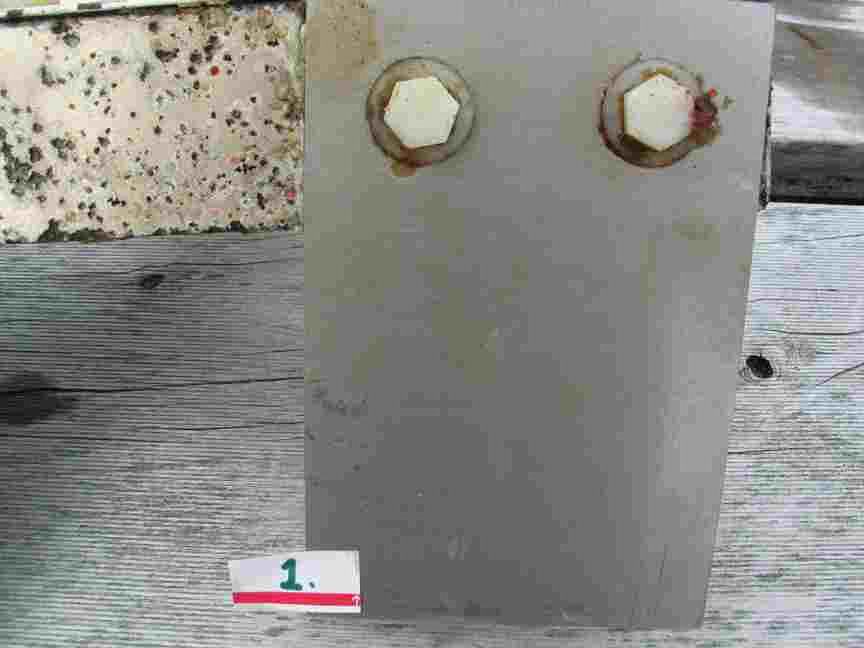
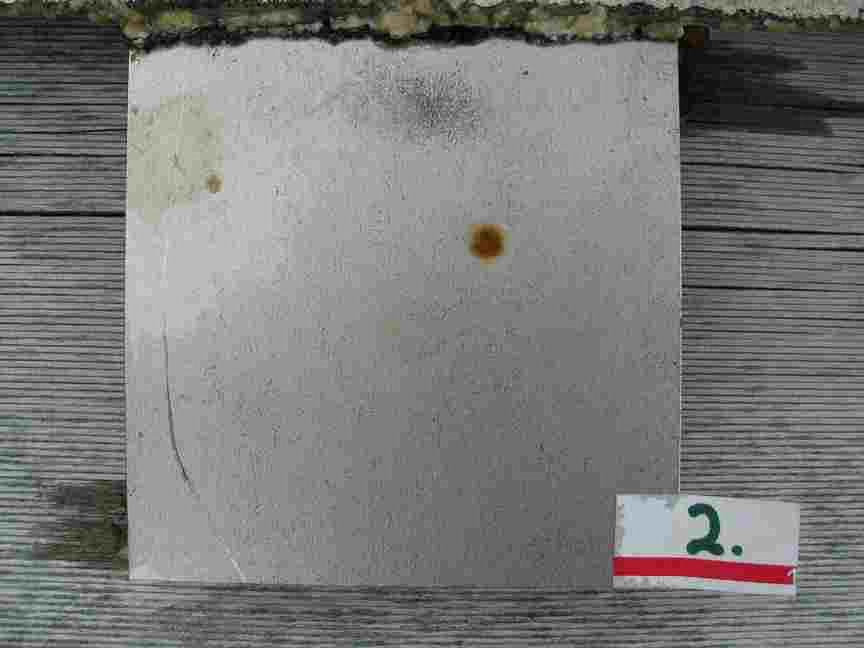
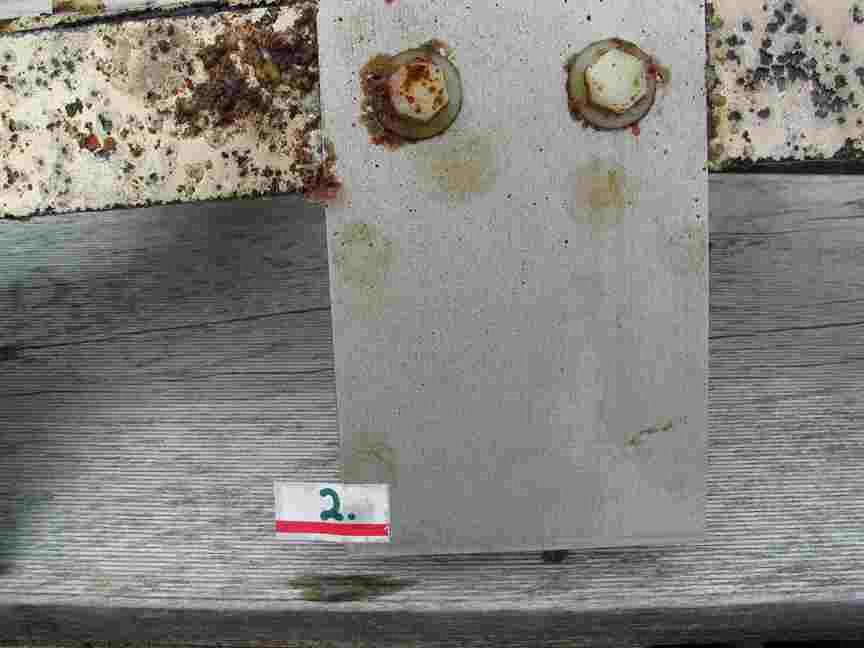
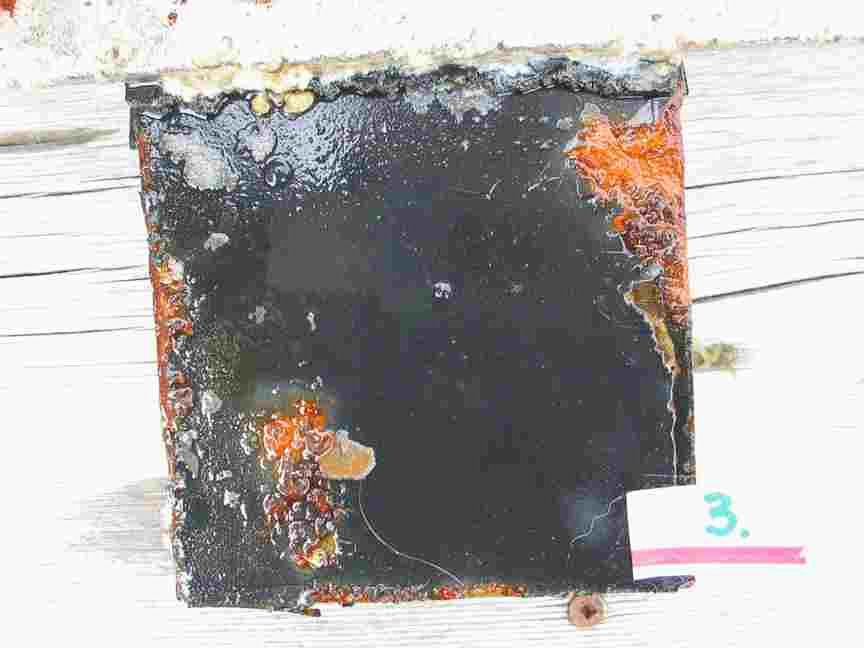
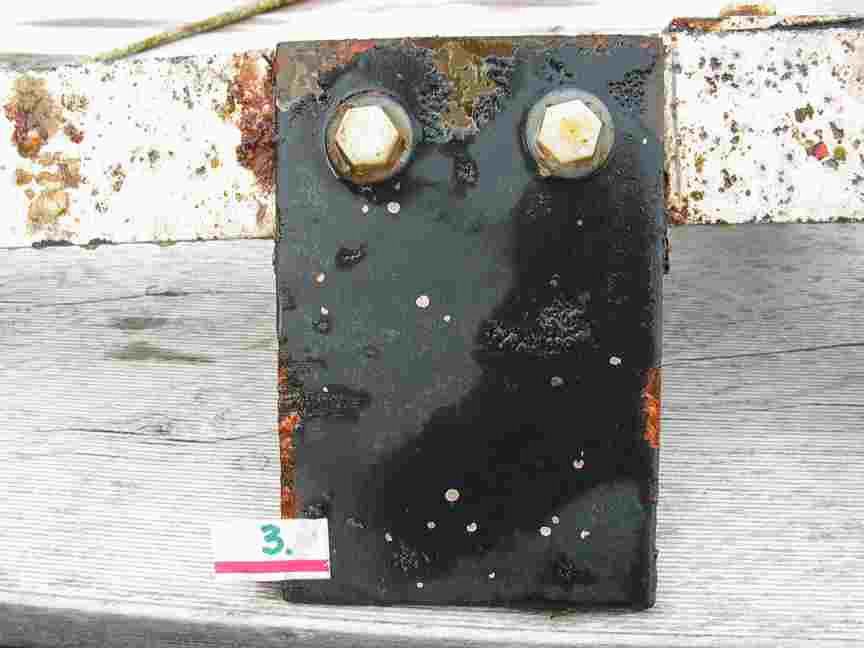
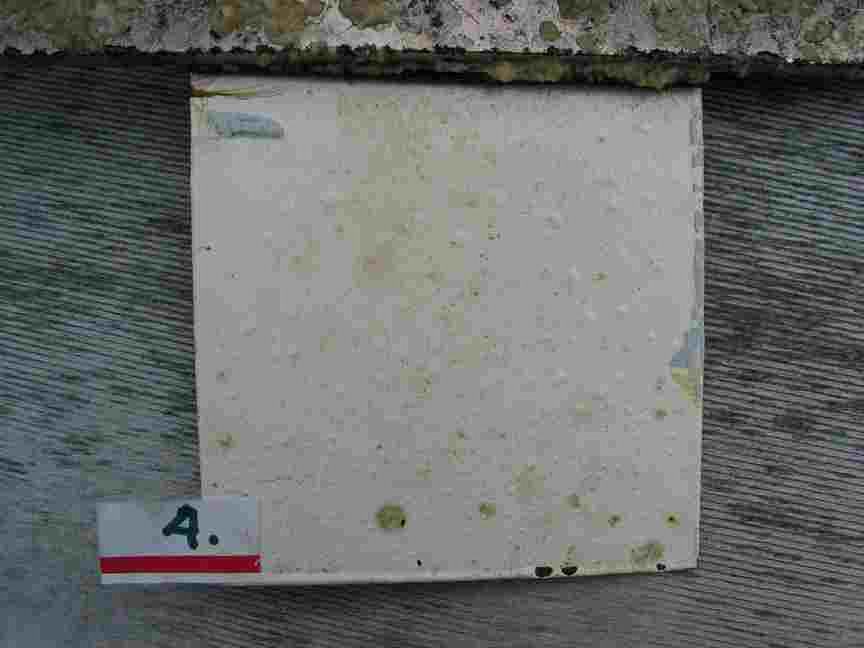
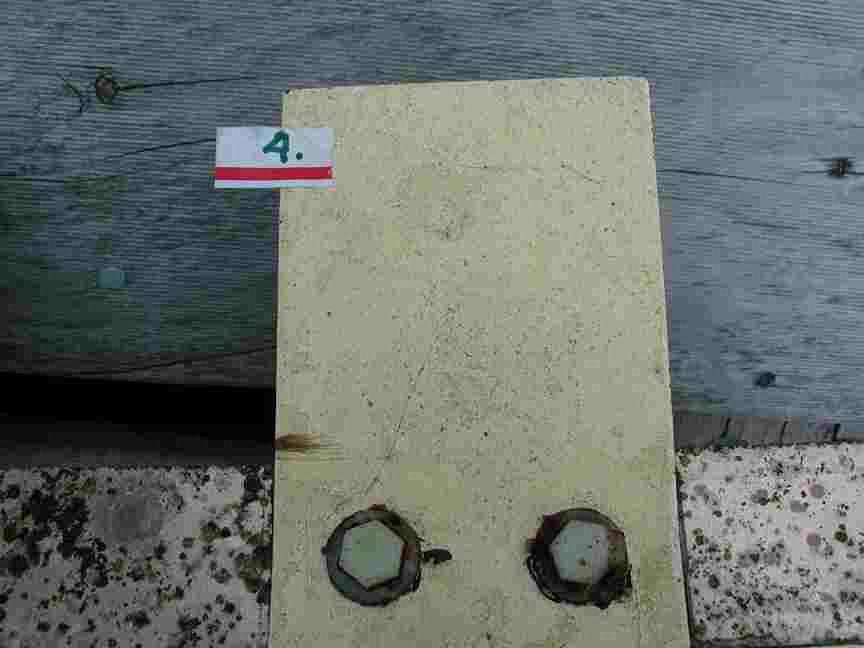
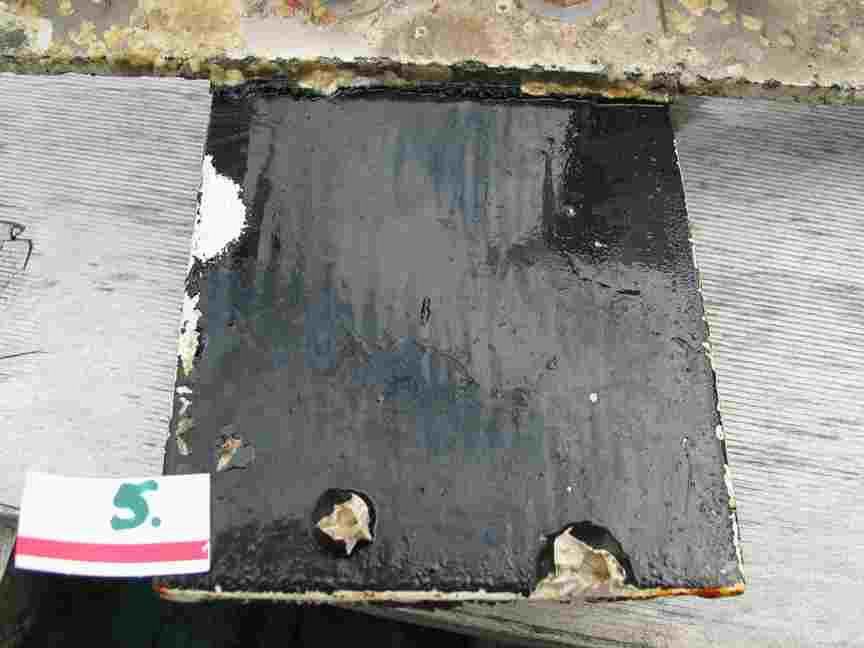
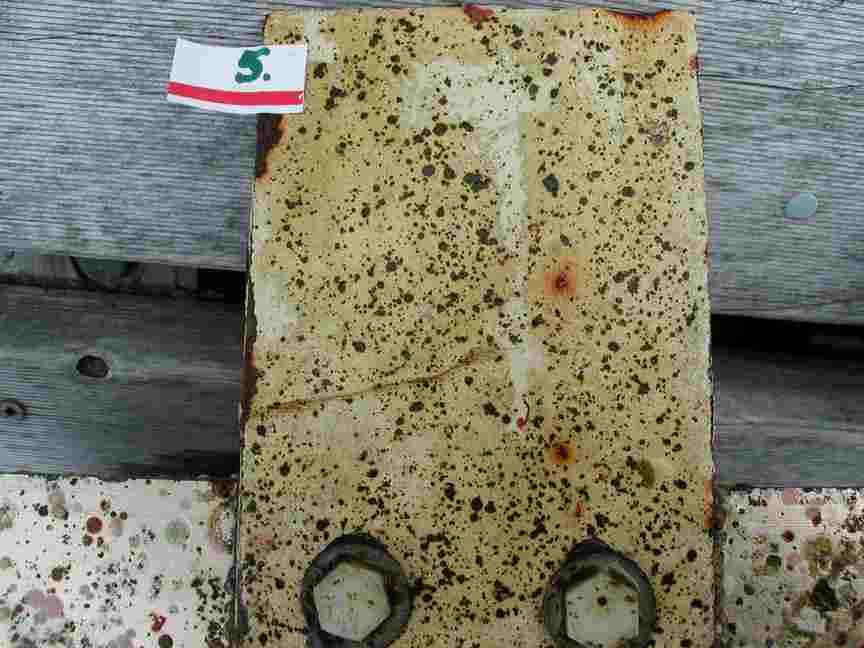
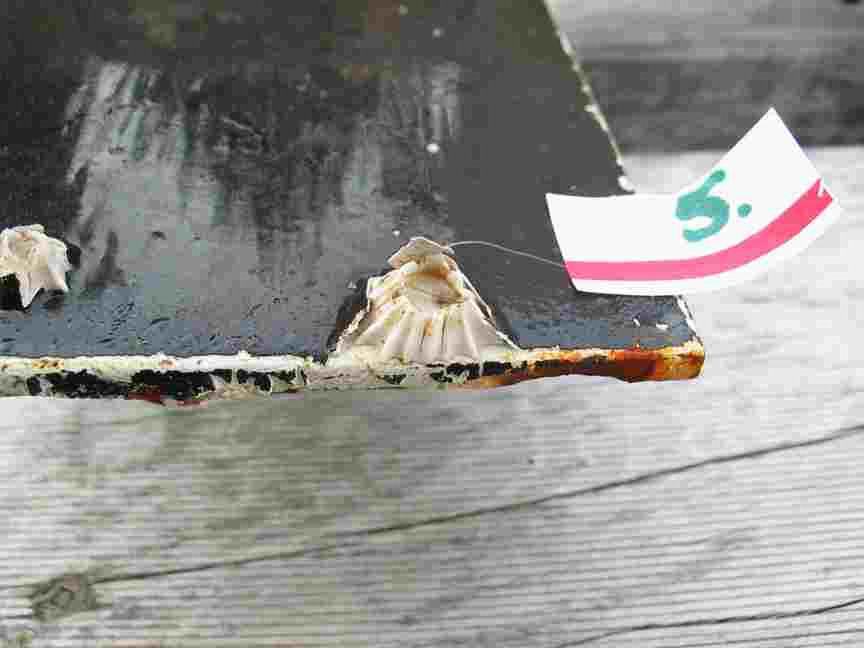
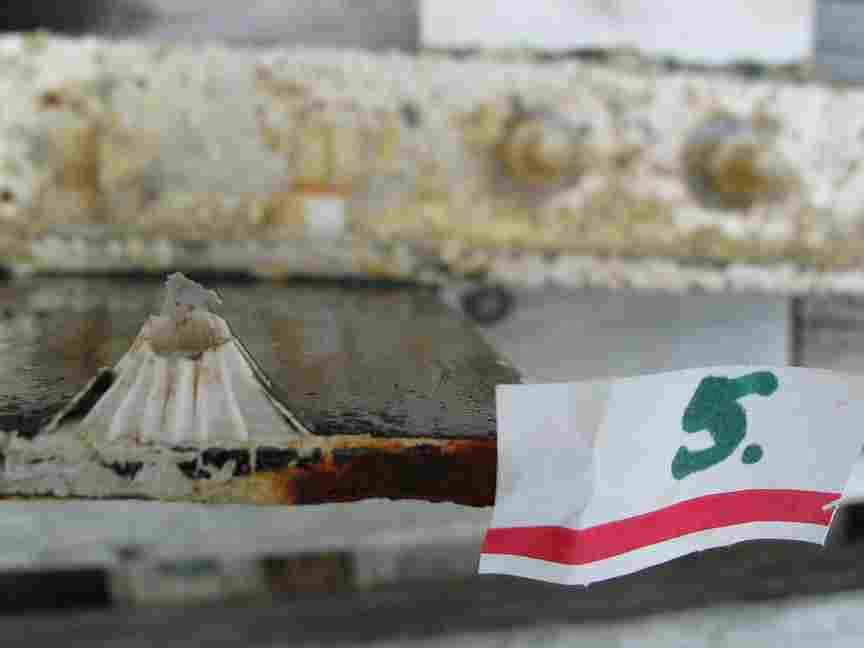
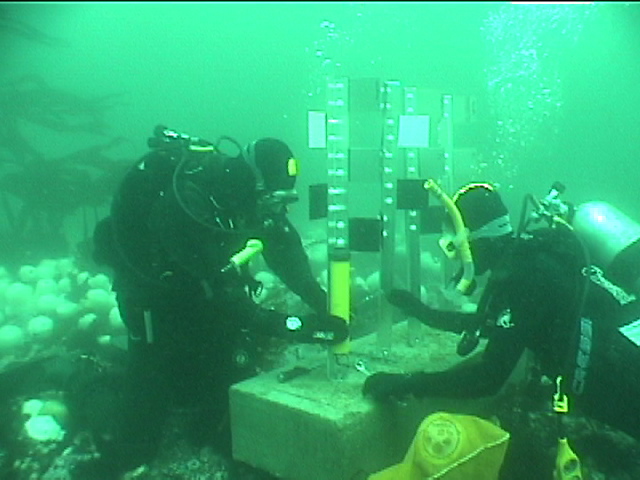 The engineers concern for the kind of materials they were going to use in constructing the turbine were addressed by having the Pearson College Divers install a series of succession plates that could be monitored for growth over several months.
The engineers concern for the kind of materials they were going to use in constructing the turbine were addressed by having the Pearson College Divers install a series of succession plates that could be monitored for growth over several months.
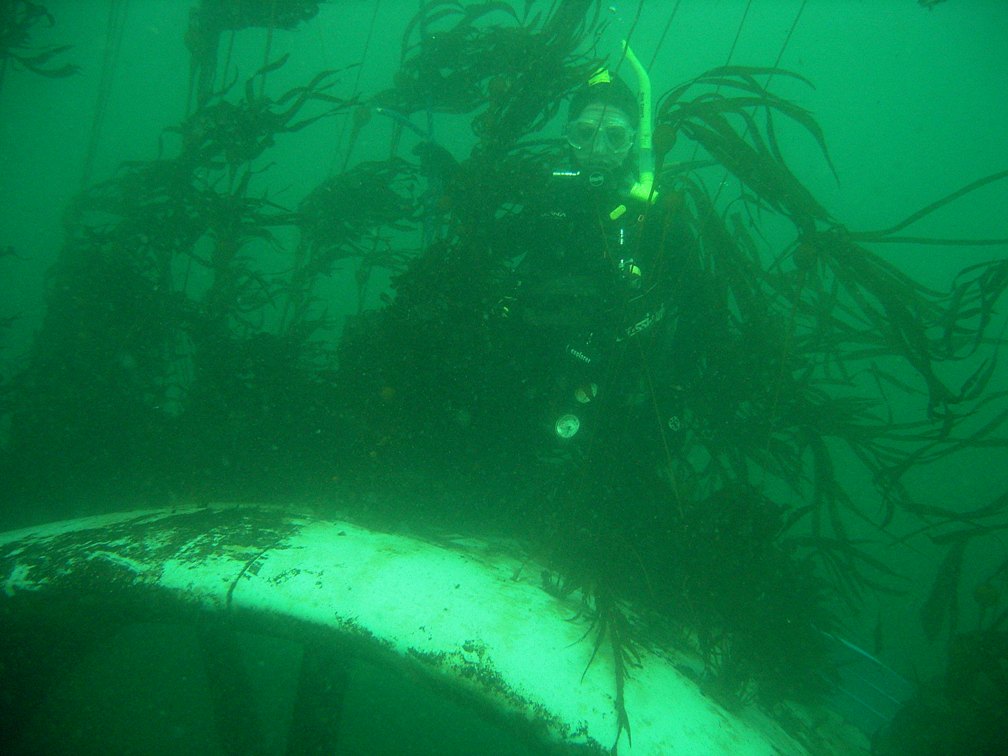
Video inspection done by Chris Blondeau on turbine inspection before removal, June, 2011 The growth of Invertebrtates is quite incredible. Since ther is little opportunity for predators like starfish to browse on this column, growth is unimpeded. This led us to decid that the i meter wide .. 15 metre high column should remain in place after the turbine was removed as such it has turned out to be such a unique habitat.
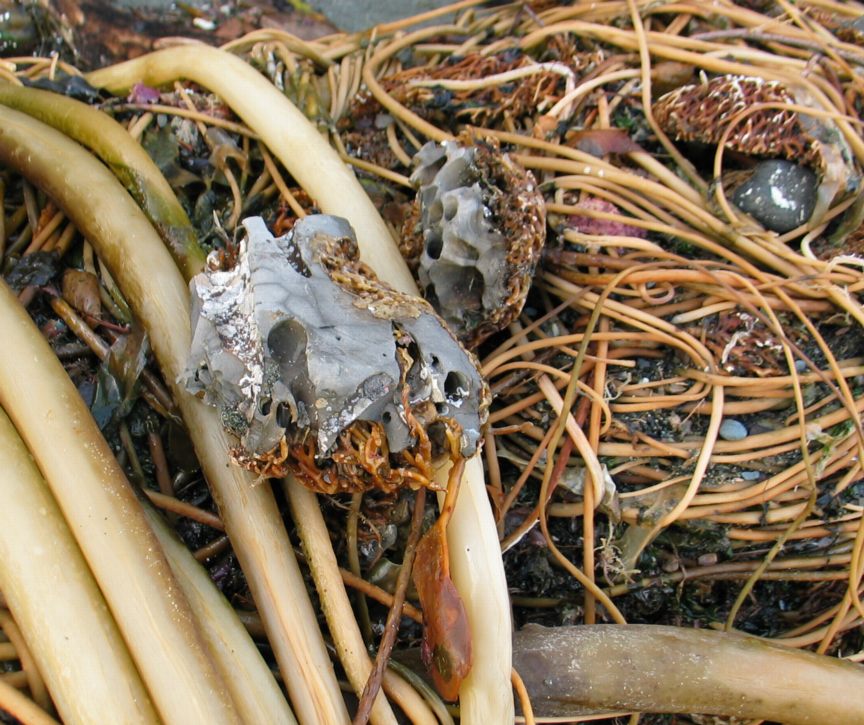
Another example of succession is evident in the way that kelp attaches to a solid substrate and can end up in modifying the environment. In this case moving rocks from ocean to shore.