Weather:
- Sky overcast, some clear patches (not much solar power generated today)
- Visibility 15+ miles, no fog
- Wind 10-20 knots W
- Water calm. Some interesting standing wave patterns lately.
Boats/Visitors:
- On Thursday Greg came in the afternoon to top up our water supply. Pearson alum Norbert (currently alum in residence) also came along for the ride to check out our solar panels and provide suggestions for future improvements. Pearson maintenance volunteer Jimmy also stopped in for the night to visit race rocks before he goes home to Mexico. Safe travels!
- We had many hands on deck, so we were able to successfully repair and raise the flagpole.
- Yesterday Greg visited with a group of college guests who toured the island.
Ecological:
- The sea lions have started to haul out on the N + S/SW sides of Great Race Rock.
- The oyster catcher chicks have grown to be nearly as big as their parents and are flying all over!
- The seagull chicks are getting bigger and when rival adults attack they now fight back. On Thursday we spotted a chick with one eye pecked out and were concerned that it would not survive. Fortunately, when we checked later it was doing well.
- There have been large numbers of black turnstones present this past week, 30+ at once
- Seagulls eating sea urchins
- closer view
- Male elephant seal having a soak on the jetty
- Seagull bathing
- Elephant seal on jetty
- Signs of moulting skin and fur
- California sea lions swimming
- A small boat far from safety in the currents of race passage and very close to the sea lions.
- Siblings hatched within 2 days of each other, one much smaller.
- Black turnstones
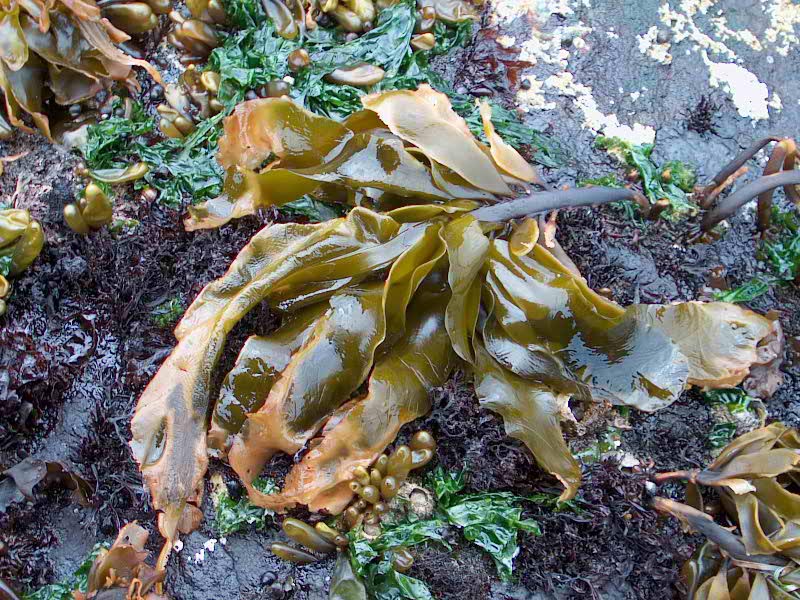
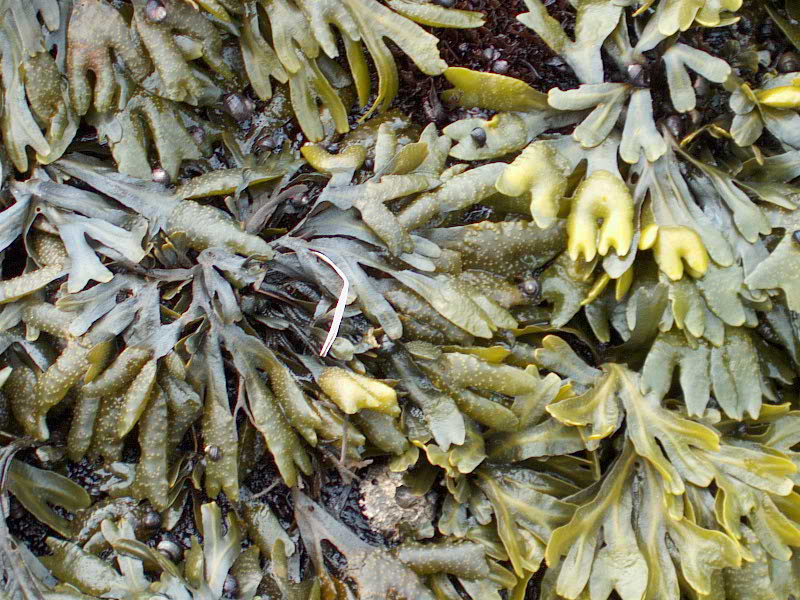
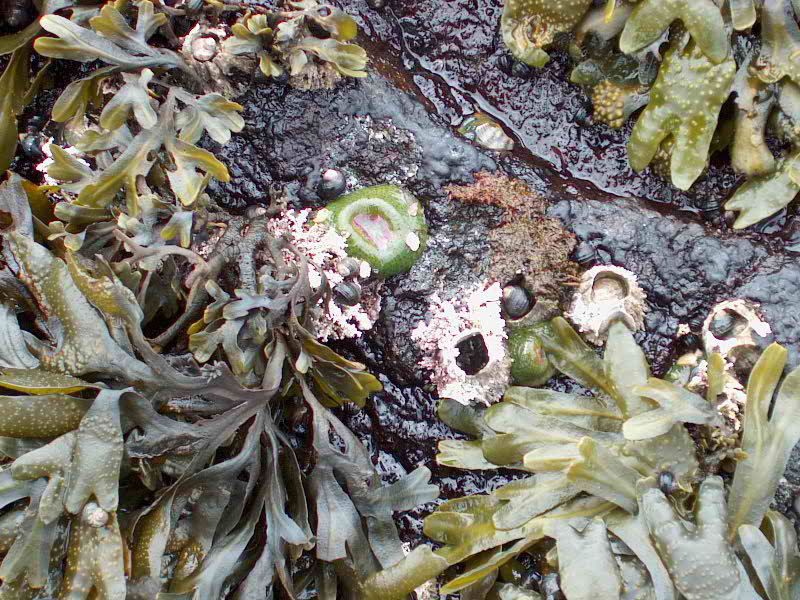
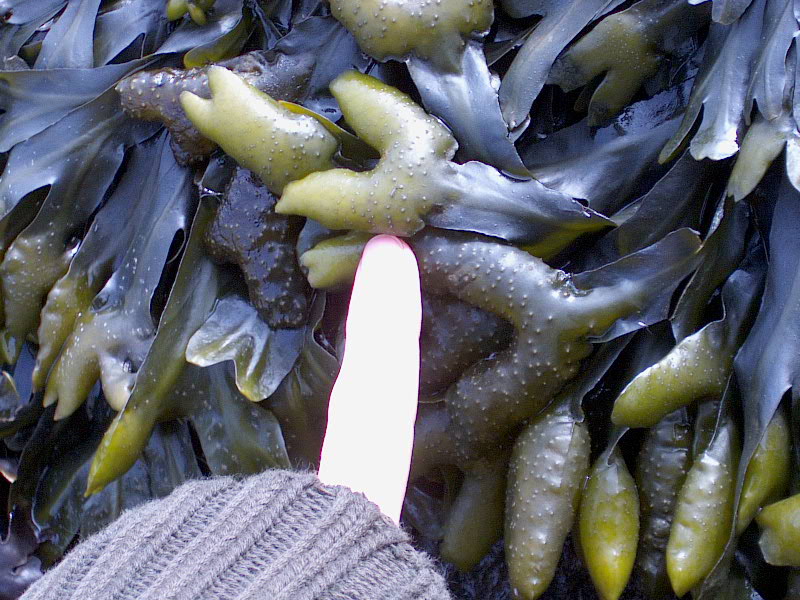
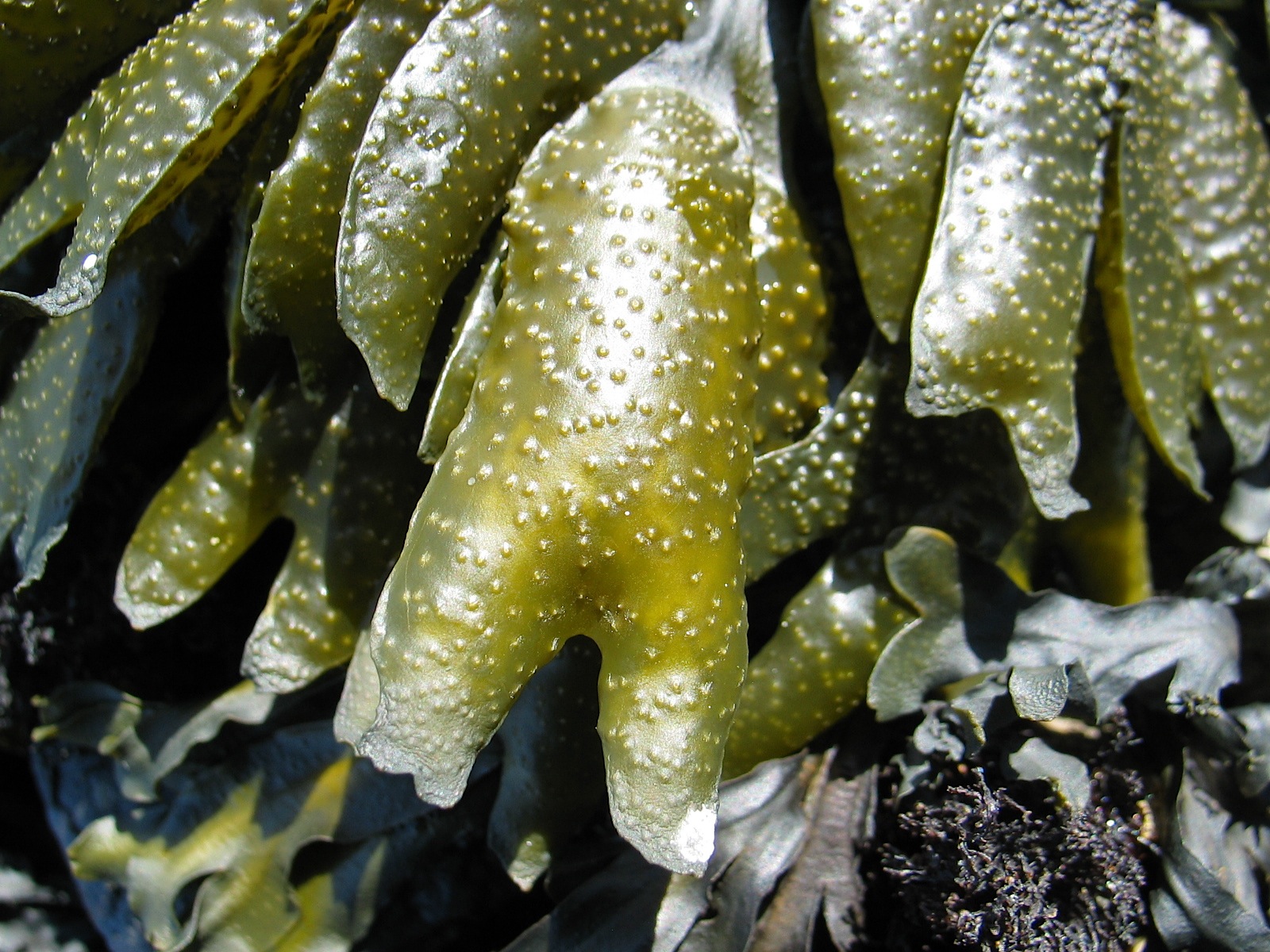
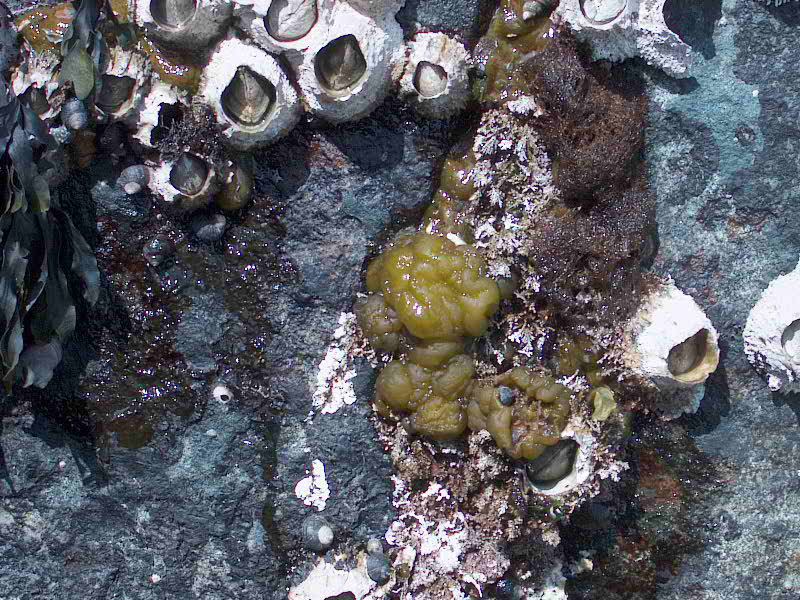
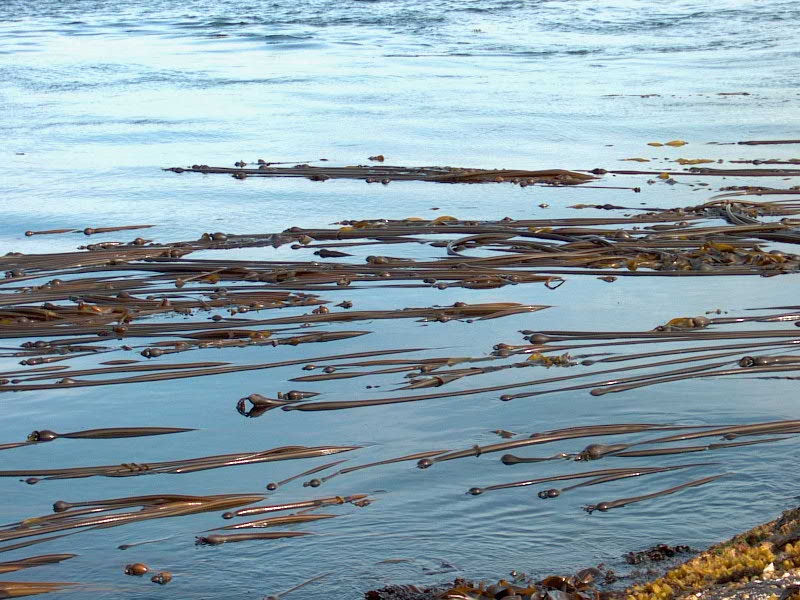
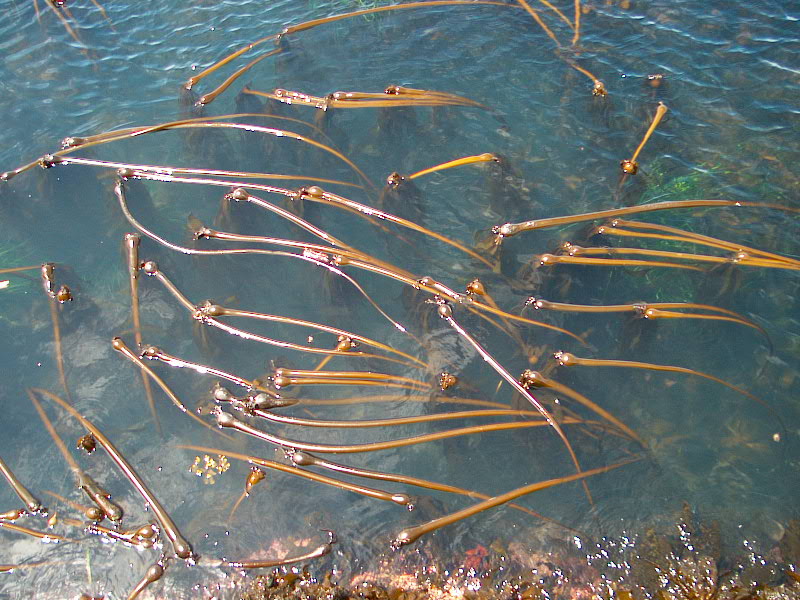
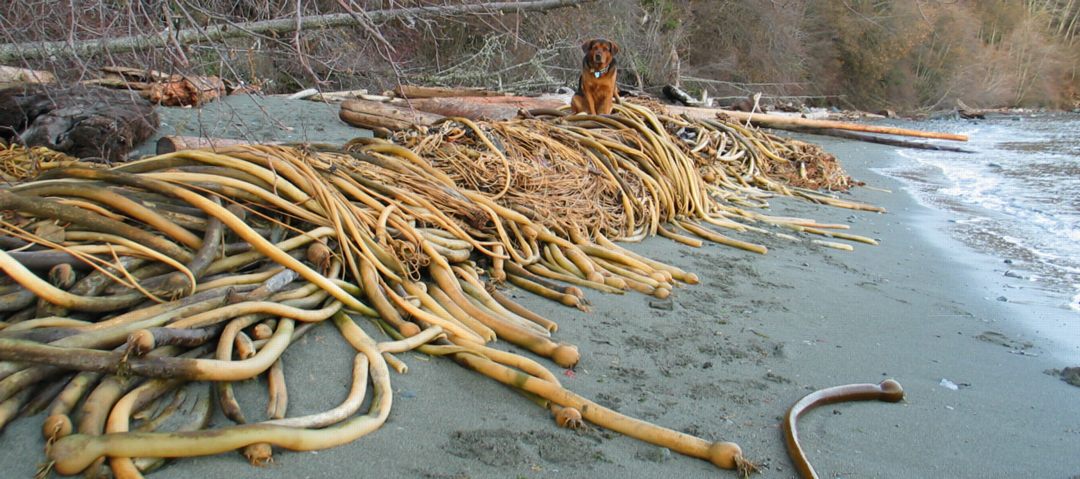
- Seersucker kelp on the jetty
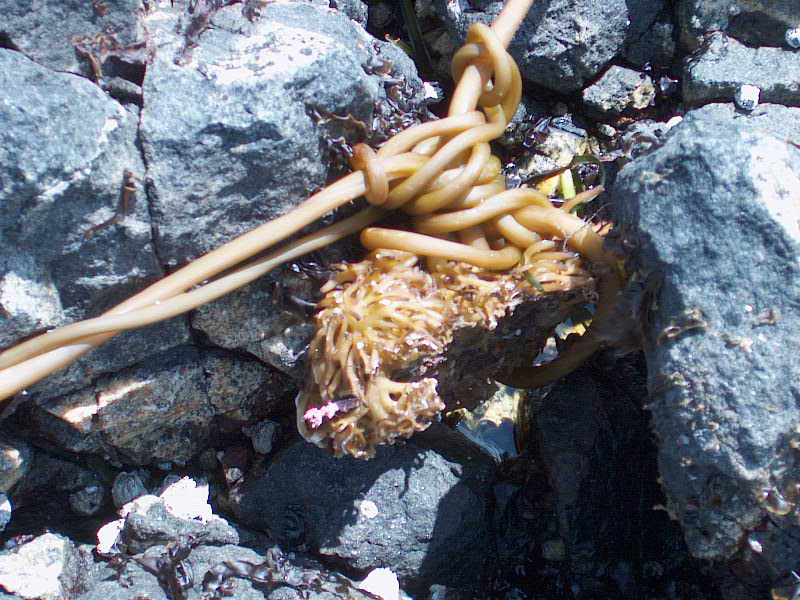
- Gumboot chiton
- Gull catching drips of fresh water
- One of the fish a gull regurgitated to feed its chicks
- Blooming english stonecrop
- Abandoned nest near jetty. Eggs did not hatch and mother is missing.
- Flagpole back in order