Obituary: Trevor Anderson: James Bay fixture was a lighthouse keeper, sailor and war veteran
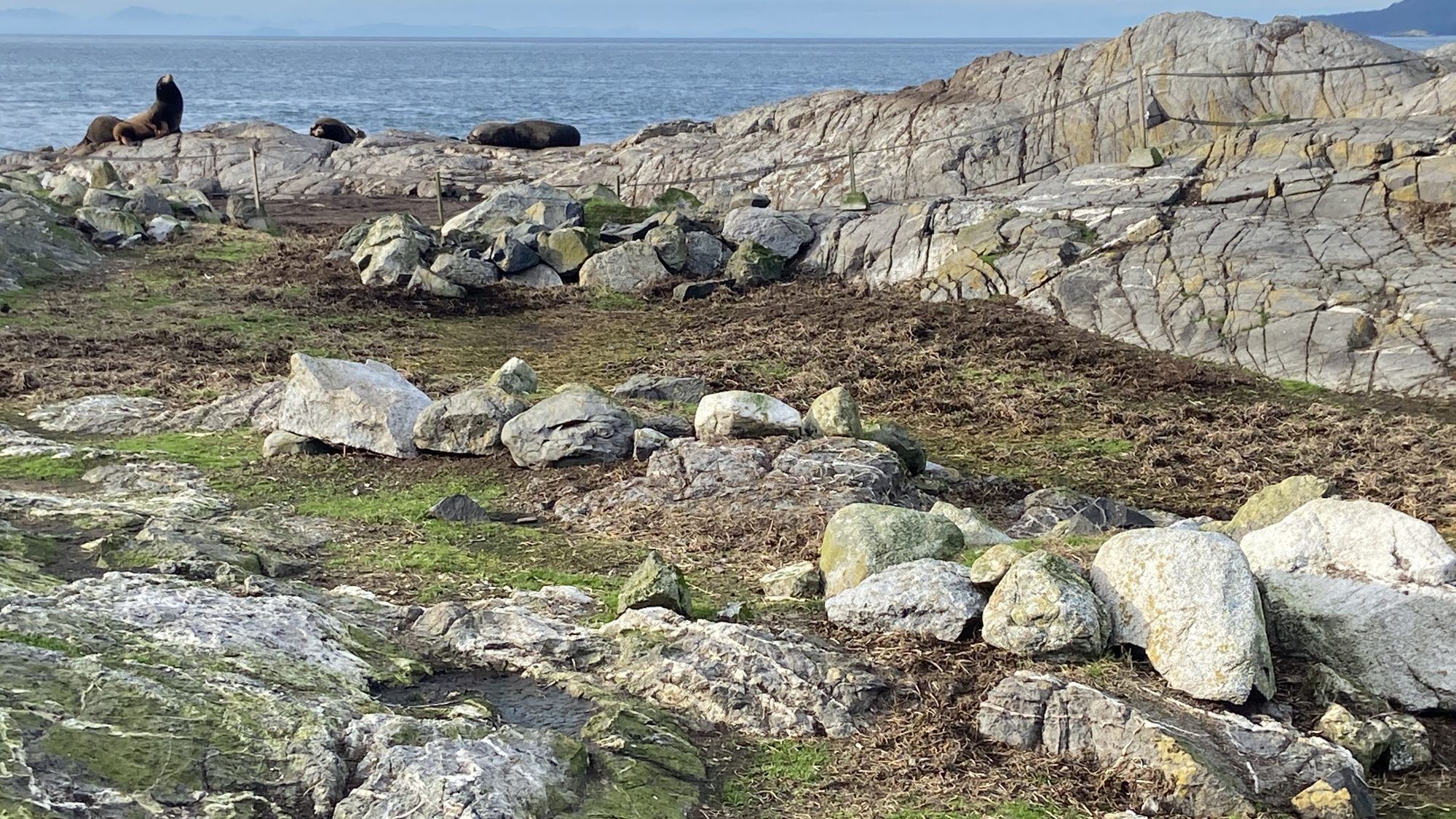
It was in the late 1970s that Trev and Flo Anderson convinced us at Lester Pearson College that we should seek some form of protection for the unique ecosystems at Race Rocks. It was as a result of their urging that we worked to get the Archipelago of islands at Race Rocks designated as a provincial Ecological Reserve in 1980.

Link to the Victoria Times Colonist article
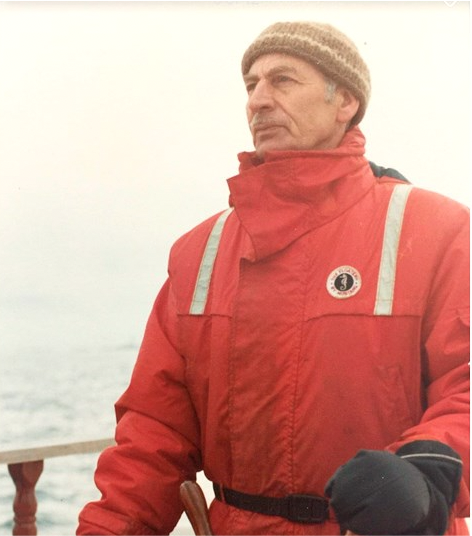
For more than 15 years, Trev Anderson was a fixture in James Bay, sitting in his favourite chair on the front porch of his Niagara Street home in his signature black hat, waving, chatting and even blowing the odd passersby a kiss.
In return, Anderson, who died Monday at the age of 103, got to pet all the dogs in the neighbourhood and a chance to taste a sampling of brownies for his sweet tooth.
Those he greeted would have little idea of the colourful life the friendly senior had lived.
That life included narrowly escaping after his plane was shot down in the Second World War, becoming a lighthouse keeper in the early 1960s, and building a 55-foot sailboat to live on board for eight years — despite little knowledge of how to sail.
“My dad was vivacious up to the end — that’s just how he lived life,” said Adrianne Lowden, the youngest of Anderson’s four children with wife Flo (Florence), who died in 2017.
“He was as tough as nails but he also had an incredible sense of humour.”
Trevor Maxwell Anderson was born in Regina, Sask., on Oct. 22, 1920. His family moved to northern British Columbia when he was around six and he spent some of his teenage years in Shawnigan Lake, finally moving to Victoria in his late teens.
He enlisted in 1941, receiving training as a wireless operator and gunner. He was stationed in Egypt, Libya, Tunisia and Sicily, flying in B-25 bombers attached to the Royal Air Force.
When not operating the Morse code machine, he was responsible for two 50-calibre machine guns in the bomber’s belly.
His plane was shot down on his fourth mission, crash-landing in the Mediterranean Sea — there is a picture of the stricken plane, taken from another plane in the formation, on the wall of his James Bay home.
“Dad told me that the only way out was through a 10-inch [square] window — he remembered kicking it,” said Lowden.
She said that her father can’t recall how he managed to fit through the small opening, as he was wearing heavy gear to keep out the cold and an inflatable jacket as well.
All the crew survived the crash and scrambled onto a life raft. They were picked up by a fishing boat, but the engine died, delaying their return to dry land for three days.
The experience did not deter Anderson from returning to the air. He completed a total of 55 missions, with the usual number for gunners typically running 25 to 30.
It was during his tour of North Africa that he began to write to Flo, his future wife.
In one of the letters, he asked her to marry him — and she accepted. They married in 1944 and the two were together until Flo’s death.
He enlisted with the Air Force upon his return from North Africa, retiring in 1960.
The following year, with Flo and two boys and two girls in tow, he became a lighthouse keeper, initially on Lennard Island, on the southwest entrance to Templar Channel, north of Tofino.
The family became “rock hoppers” stationed at various lighthouses, including Green Island, 40 kilometres northwest of Prince Rupert, the northernmost lighthouse that was staffed.
In 1966, they were assigned to Race Rocks, where they remained until Anderson retired for the final time in 1982.
While he was on Race Rocks, he got the notion of building a sailboat, though he was a novice sailor.
It took the couple seven years to build a 55-foot ketch — a two-masted sailboat — which they christened WaWa.
They learned to sail, cruising the Gulf Islands and circumnavigating Vancouver Island before heading to the South Pacific in 1985.
“My parents gave us incredible lives,” said Lowden. “My siblings and I had the fortune to grow up fully and share the adventure.”
She said both her parents wrote books about their experiences. Her mother wrote an autobiography called Lighthouse Chronicles about the lighthouse years, while her father wrote The War and I about his wartime experiences, with both of them collaborating on All At Sea about their time on the water.
After their South Seas adventure, they returned to Victoria in 1987, living aboard WaWa for another eight years. After selling the boat, they jumped into a camper and travelled around North America until 1999, when they returned to Victoria.
The couple settled into the 1904 house on Niagara Street that Flo’s parents had originally bought in 1959.
That’s where Anderson would sit on the front porch and greet passerby from his favourite old armchair. Once he determined that the neighbourhood was safe and secure, he would retire for his afternoon nap.
“He was up and about until about two weeks ago,” said Lowden
Since his 100th birthday, Anderson’s children, Adrienne, Beth, Stan and Garry, have been putting up a banner on the front porch saying “TREV, Happy Birthday,” followed by his age.
This week, the birthday wishes were replaced with Bon Voyage as a send-off for a life well-lived.
parrais@timescolonist.com
>>> To comment on this article, write a letter to the editor: letters@timescolonist.com
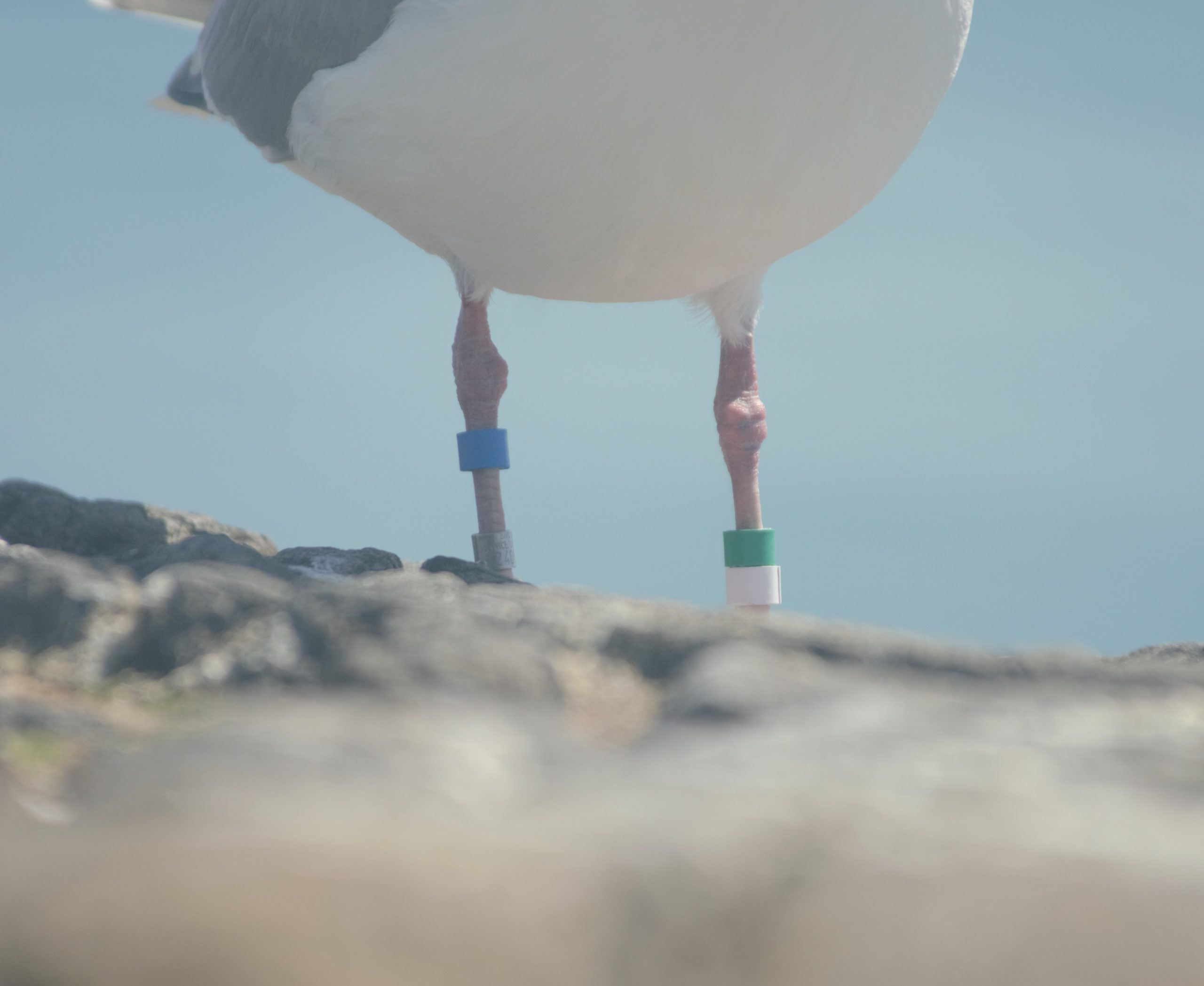
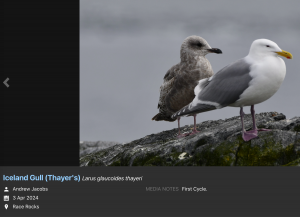
 I got a ride out on Second Nature with Greg and we also took out two bird observers from the Rocky Point Bird Observatory ( RPBO) / BC Nature Gull survey, Andrew Jacobs and James Kennerley. The detailed observations and a link to the identification of the interspecific gull hybrids eBird Canada Checklist – 3 Apr 2024 – Race Rocks – 16 species (+2 other taxa) was a valuable addition to research in the Ecological Reserve. Below is a sample from Andrew’s photos on eBird of their identification of the different gulls:
I got a ride out on Second Nature with Greg and we also took out two bird observers from the Rocky Point Bird Observatory ( RPBO) / BC Nature Gull survey, Andrew Jacobs and James Kennerley. The detailed observations and a link to the identification of the interspecific gull hybrids eBird Canada Checklist – 3 Apr 2024 – Race Rocks – 16 species (+2 other taxa) was a valuable addition to research in the Ecological Reserve. Below is a sample from Andrew’s photos on eBird of their identification of the different gulls: