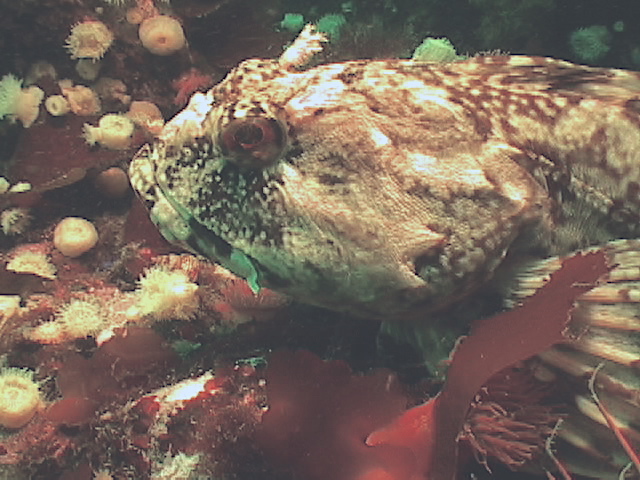
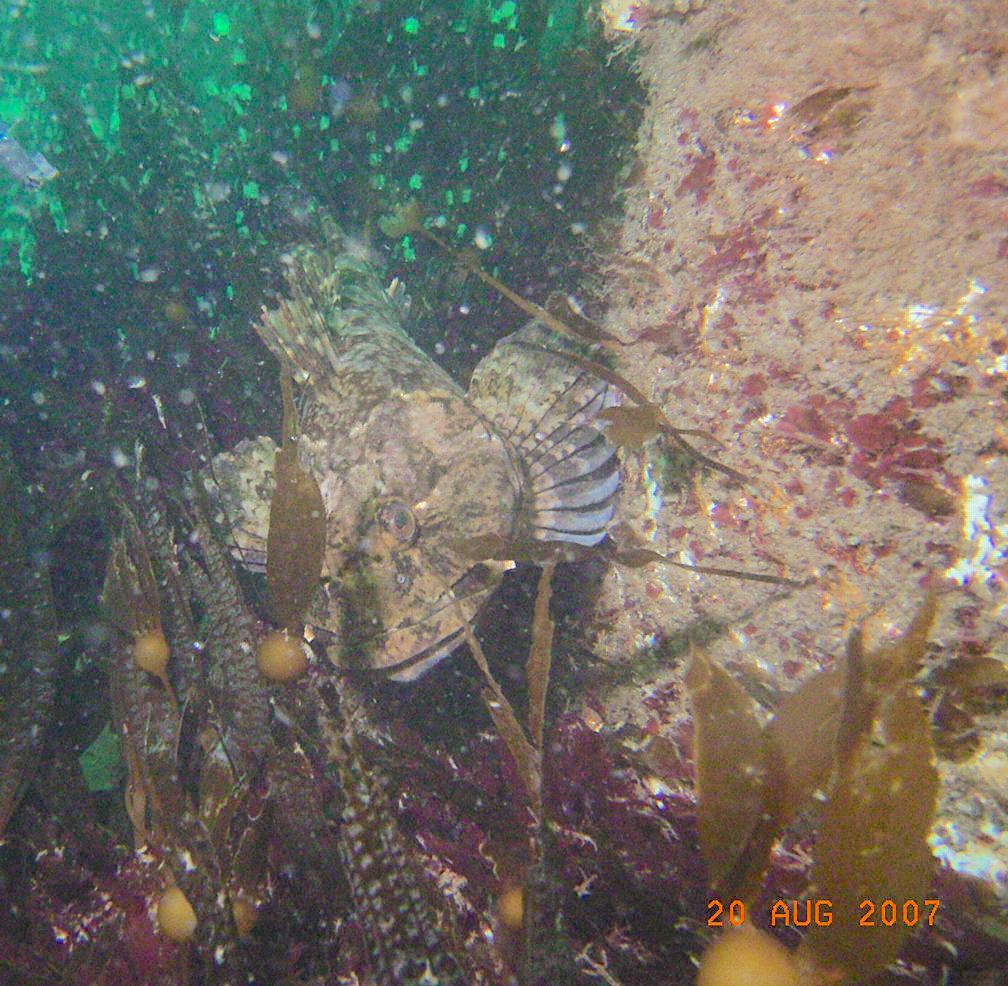
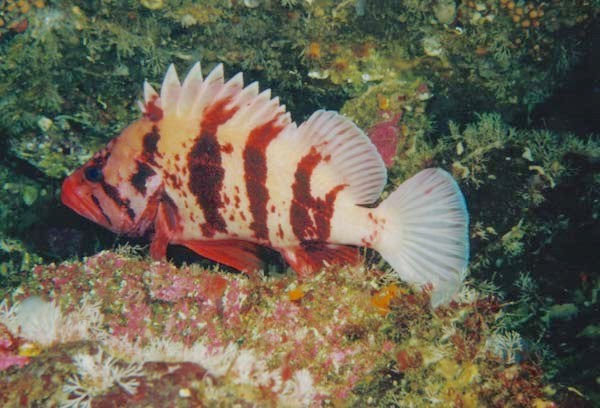
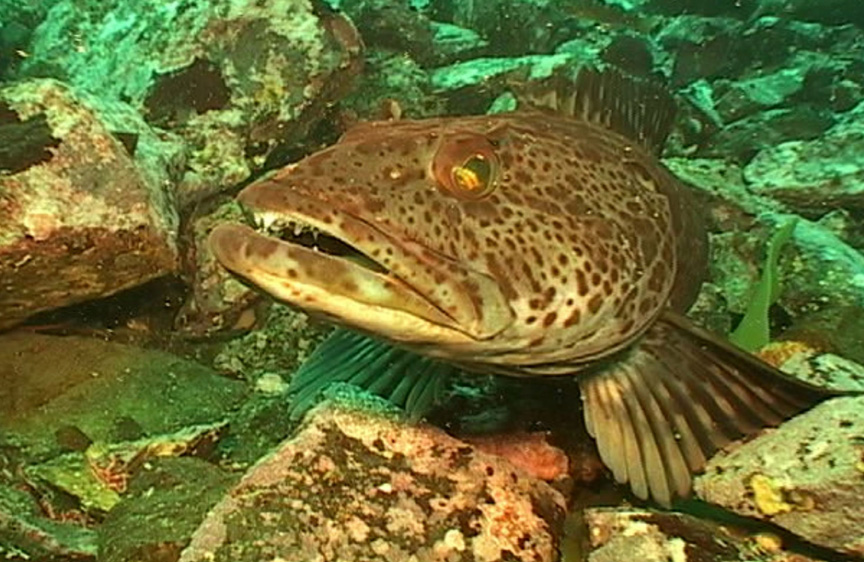
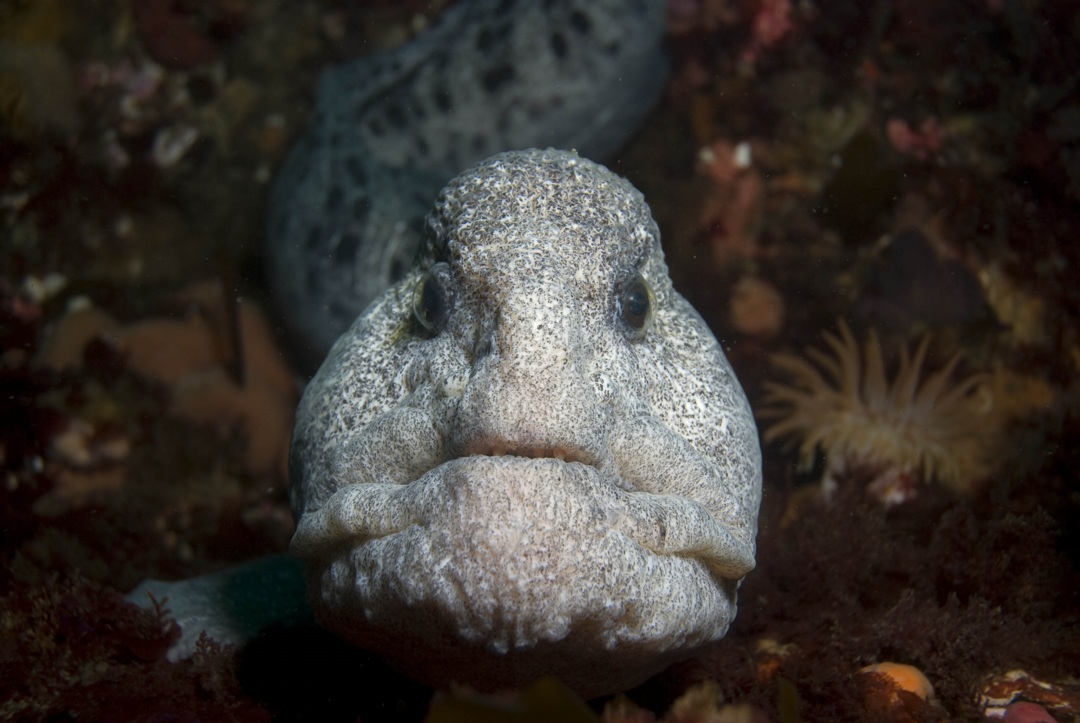
- By August of 2007, a Cabezon has taken up a territory on the Tidal Energy Piling. Photo by Chris Blondeau.
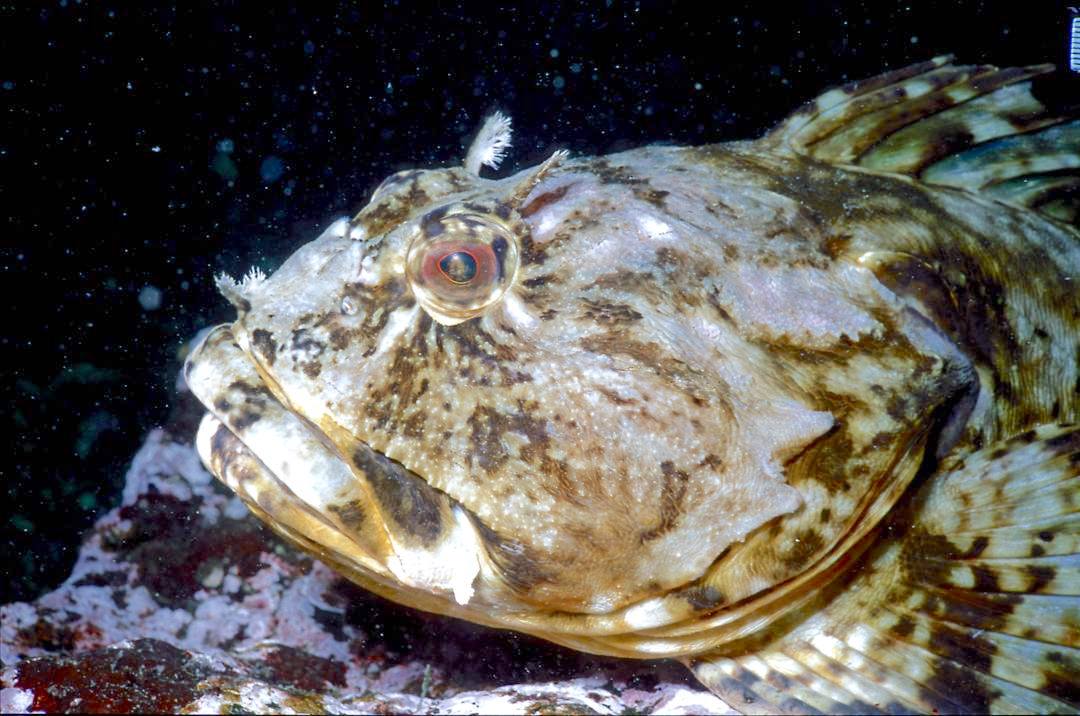
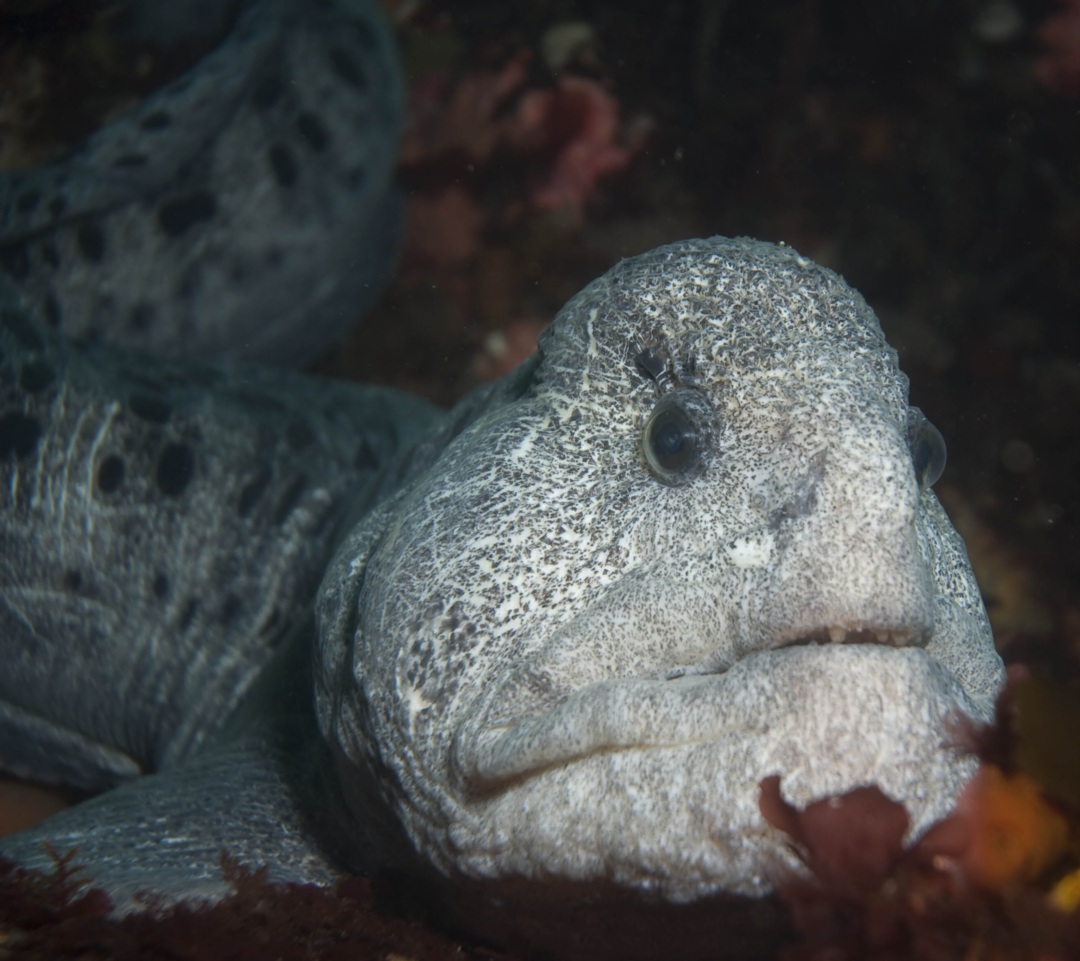
- Cabezon taken underwater at Race Rocks Head of Cabezon: photo by Dr. Armin Svoboda
Cabezon:(literally big head in Spanish ) is a benthic fish that lives among the kelp holdfasts and rocky areas, usually very close to the bottom. It is often so confident of its camouflage that it will not move when approached by divers. Note the multi colored eye. These fish will lunge at almost anything that moves on the bottom. Dissections of their stomachs reveal amphipods and small crabs, pieces of kelp (and even rocks they have grabbed when foraging for other invertebrates.)
Cabezon are normally benthic or bottom-dwellers, living among rocks and seaweeds in tide pools. Sometimes they live just below the water’s surface among the marine plants. Their coloration allows them to remain well camouflaged. Their habitat is most likely rocky, sandy and muddy bottoms, living in areas with a depth range of 0 to 200 meters. Moreover, young cabezon feed on small crustaceans like amphipods, shrimp, and crabs. The adults feed on crustaceans, marine worms and mollusks, including clams and abalone. They can swallow a whole abalone and later regurgitate the indigestible shell; therefore, their tropic level is that of a secondary carnivore. In addition, the limiting factors that will affect the development and growth of this population in a certain habitat will be the presence of enough light, temperature and the availability of food and living space
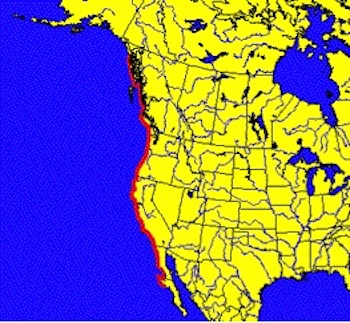 Their maximum length and weight are 99.0 centimeters and 14.0 Kilograms respectively. This organism can be seen in the Eastern Pacific, which covers the areas from Southeastern Alaska to Punta Abrejos, in Central Baja California, Mexico. Race Rocks is located in the centre of this range. In this map we can see the range of this fish.
Their maximum length and weight are 99.0 centimeters and 14.0 Kilograms respectively. This organism can be seen in the Eastern Pacific, which covers the areas from Southeastern Alaska to Punta Abrejos, in Central Baja California, Mexico. Race Rocks is located in the centre of this range. In this map we can see the range of this fish.
Reference The National Biological Information Infrastructure (NBII) BioBot
http://www.elasmodiver.com/BCMarinelife/BCML%20Chordata.htm
|
Other Members of the Class actinopterigii/ at Race Rocks.
|
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. March 15 2005- Diomedes Saldana PC -Greco The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. March 15 2005- Diomedes Saldana PC -Greco |